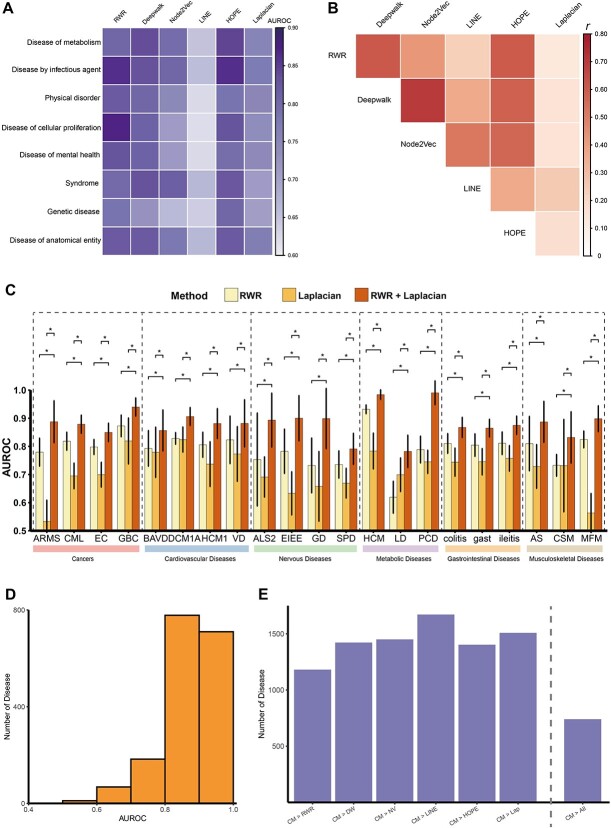
Figure 3.
The efficiency varied among different gene distance in identifying disease signals. (A) Difference in the disease signal detection efficiency of six algorithms across eight disease categories. (B) Pairwise correlation between the efficiency of different methods for exploring disease signals. r: Pearson correlation coefficient. (C) Combining of algorithms can improve the effectiveness of exploring disease signals for certain diseases. AUC comparison for various methods (RWR, Laplacian, combined RWR with Laplacian) through different type of diseases. ARMS: alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, CML: chronic myeloid leukemia, EC: esophageal cancer, GBC: gallbladder cancer, BAVD: bicuspid aortic valve disease, DCM1A: dilated cardiomyopathy 1A, HCM1: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 1, VD: vascular disease, ALS2: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 2, EIEE: early infantile epileptic encephalopathy, GD: generalized dystonia, SPD: secondary Parkinson disease, HCM: hypercalcemia, LD: Leigh disease, PCD: pyruvate carboxylase deficiency disease, gast: gastroenteritis, AS: ankylosing spondylitis, CSM: congenital structural myopathy, MFM: myofibrillar myopathy, *: P-value <0.05. (D) AUROC for the combined method based on consensus score to distinguish disease gene among 1750 diseases. Histograms were used to describe the AUROC distribution. (E) Number of the diseases where consensus score outperforms individual score or any single scores. CM: Combined method based on consensus score, RWR: random walk with restart, DW: Deepwalk, NV: Node2Vec, Lap: Laplacian methods, CM > ALL: the consensus score exceeds any single scores.