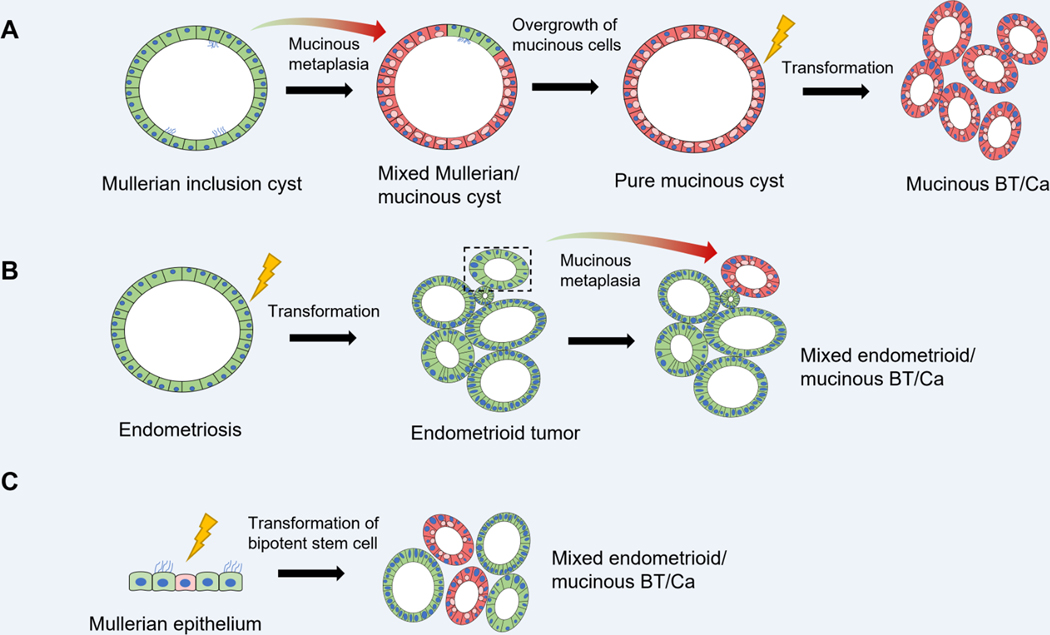
Figure 6:
Proposed models of pathogenesis for pure and mixed gastro-intestinal type mucinous ovarian tumors originating from Mullerian epithelial precursors. (A). Transdifferentiation of a subset of cells within a benign Mullerian-type cyst, resulting in a mixed gastrointestinal-type mucinous / Mullerian cyst. Eventual replacement of the entire cyst lining by mucinous cells could potentially result in a pure mucinous cystadenoma, which may serve as the substrate for development of mucinous borderline tumors or carcinomas. (B) Endometriosis gives rise to an endometrioid borderline tumor or carcinoma, within which a subpopulation undergoes mucinous metaplasia, resulting in a mixed endometrioid / gastrointestinal-type mucinous tumor. (C) Mixed tumors can also potentially result from direct transformation of a putative bipotent stem cell within Mullerian epithelium (e.g. endometriosis, cortical inclusion cyst epithelium, etc) capable of gastrointestinal and Mullerian lineage differentiation.