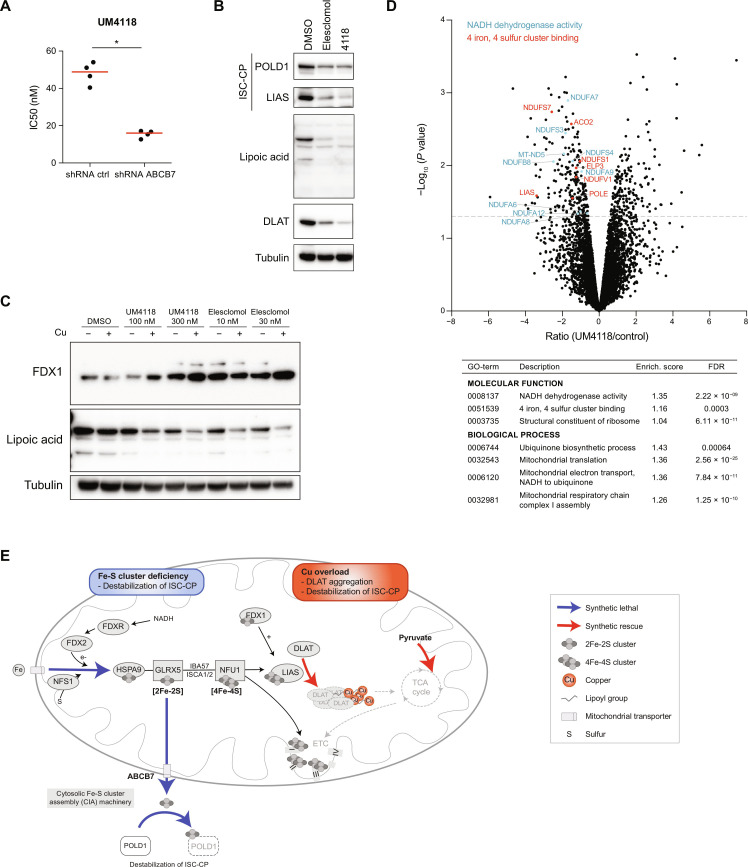
Fig. 7. ISC deficiency potentiates copper-mediated cell death.
(A) Dot plot distribution of UM4118 IC50 values in OCI-AML5 cells expressing an shRNA control or targeting ABCB7. Median is represented in red (n = 4, Mann-Whitney U test). (B) Immunoblot analysis of POLD1, LIAS, lipoic acid, and DLAT proteins on OCI-AML5 cells cultured in media supplemented with 1 μM copper and exposed 16 hours to 30 nM elesclomol, 300 nM UM4118, or DMSO. Tubulin is used as a loading control. (C) Immunoblot analysis of FDX1 and lipoic acid proteins on OCI-AML5 cells treated with indicated compounds for 16 hours, both with and without media supplementation with 1 μM copper. Tubulin is used as a loading control. (D) Total proteome analysis performed on OCI-AML5 cells exposed 16 hours to UM4118 (300 nM) in media supplemented with 1 μM copper. Data represent proteins identified in at least two peptides. Some of the most significant GO terms (STRING) are indicated in the table. Significant proteins of the “NADH dehydrogenase activity” and “4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding” pathways are highlighted (NDUFS7, NDUFS1, and NDUFV1 belong to both pathways). (E) In this simplified model, copper overload leads to the aggregation of lipoylated DLAT and destabilization of ISC-containing proteins (ISC-CP). LIAS, which mediates DLAT lipoylation, requires an ISC for its activity and is depleted upon exposure to copper ionophores. ISC deficiency caused by the depletion of key genes of ISC biogenesis causes an additional destabilization of ISC-containing proteins leading to synthetic lethality with copper overload. Key processes identified in the UM4118 CRISPR experiment showing synthetic lethality or synthetic rescue with UM4118 are represented by blue and red arrows, respectively.