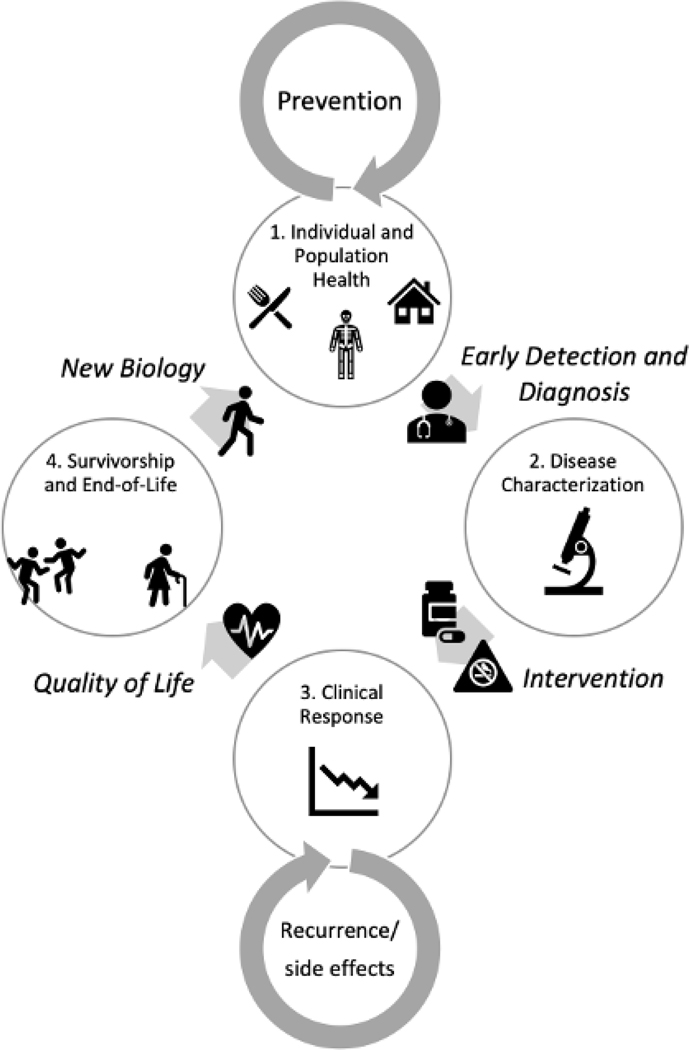
Figure 3: Individual Experience Perspective.
1. Individual and Population Health: An individual is living their life, with a certain genetic background, certain biology, in a certain place, and following certain behaviors. Some may be individual risk factors for cancer, some risks are a function of society and the environment, but all are factors that inform a person’s eventual risk. In this “pre-tumor” phase, interventions focus on prevention, lifestyle behaviors, early detection, and improving determinants at a social level in order to allow individuals to have healthy lives in an equitable, fair and just environment.
→ Early Detection and Diagnosis→
2. Disease Characterization: Some individuals may develop symptoms and be diagnosed with a tumor. As a patient, their tumor biology becomes the focus including both the characteristics of the tumor. The tumor’s microenvironment, and the interacting effects of the tumor and the broader characteristics of a patient’s biology (e.g., immune function, microbiome).
→ Intervention (Therapeutic and Non-therapeutic)→
3. Clinical Response: Intervention(s) are implemented, targeting the tumor and patient biology. Layered on targeted therapies are non-therapeutic interventions (e.g., lifestyle behaviors, integrative medicine). Here, data on clinical response, resistance, and side-effects. are important to drive clinical decisions. Another factor here is the structural framework that supports patient compliance, access to clinical trials, and continuing care.
→ Quality of Life→
4. Survivorship and End-of-life: The patient is on a quest to live a healthy life after cancer treatment, which may include symptom management, palliative care, monitoring/screening, changes in environment and behavior, and integrative medicine. These factors alter the individual biology as the patient re-enters the continuum cycle. This stage also includes accommodations and wellness measures to provide comfort and dignity to individuals at the end of their life. Inherent in discussions between patients and their caregivers is an understanding of the patient’s home and community framework that affect decision-making and adherence to interventions.
→ New Biology→ back to (1)