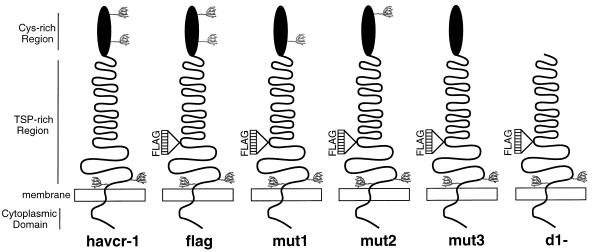
FIG. 1.
Schematic drawing of havcr-1 mutants. The extracellular domain of havcr-1 is composed of an N-terminal Cys-rich region that has homology to members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and a TSP-rich C-terminal region that contains 27 repeats of the consensus PTTTTL, which resembles mucin-like molecules. There are four putative N-glycosylation sites in havcr-1 (tree-like structures): two in the Cys-rich region and two in the TSP-rich region. Synthetic oligonucleotides coding for a FLAG peptide were inserted into the unique NcoI site of the coding region of the HAVcr-1 cDNA in the TSP-rich region, between the end of the hexameric repeats and the transmembrane domain, and the receptor was termed flag. The N-glycosylation mutant receptors mut1, mut2, and mut3 differ from flag in their numbers and positions of N-glycosylation sites in the Cys-rich region. The Cys-rich region of flag was deleted, and the resulting receptor was termed d1−.