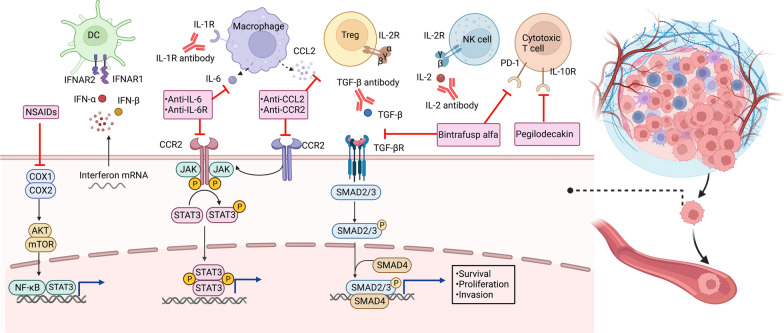
Fig. 3.
Molecular mechanisms that mediate the effects of inflammation-targeting strategies in cancer. These inflammation-targeting strategies inhibit the COX, JAK/STAT, and TGF-β signaling which support cancer cell survival, proliferation, and invasion. Figures created with BioRender. NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; COX, cyclooxygenase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; CXCR, CXC-chemokine receptor; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TGF-βR, TGF-β receptor; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SMAD, mothers against decapentaplegic