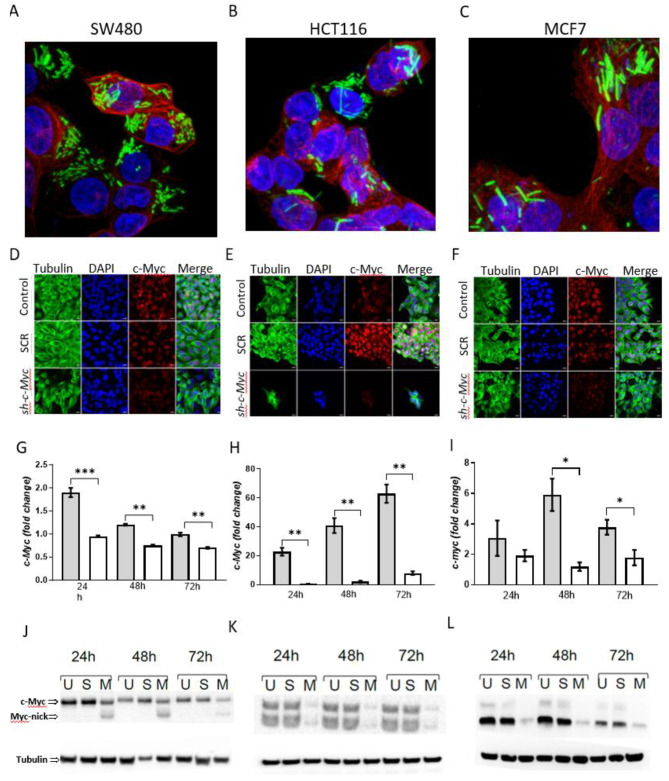
Fig. 2.
Bacterial-mediated RNAi of c-Myc in colorectal and breast cancer cell lines. (A-C) Immunofluorescence staining demonstrating intracellular infection of cell lines SW480, HCT116 and MCF7 (Red-B-actin; Blue-DAPI & green-bacteria). (D-F) Immunofluorescence staining demonstrating nuclear specific reduction of c-Myc protein at 24 h, 48 and 72 h following infection with SL7207/c-Myc strains in comparison to uninfected control and SL7207/SCR (D-SW480, E- HCT116 & F-MCF7). (G-I) qRT-PCR analysis of c-Myc expression at indicated time-points after infection with SL7207-SCR (shaded bars) and SL7207-c-Myc (white bars)(G-SW480, H-HCT116 & I-MCF7). Significant reduction of c-Myc mRNA was observed at timepoints indicated, with c-Myc mRNA levels normalised to Gapdh, Hsp909a and ActB mRNAs (t-test pairwise comparisons with * = P < 0.01, ** = P < 0.001 and *** = P < 0.0001). (J-L) Western analysis of protein samples from untreated cells (U), cells infected with SL7207/scr (S), and SL7207/c-Myc (M) demonstrating a specific semi-quantitative reduction in the abundance of c-Myc (J-SW480, K-HCT116 & L-MCF7)