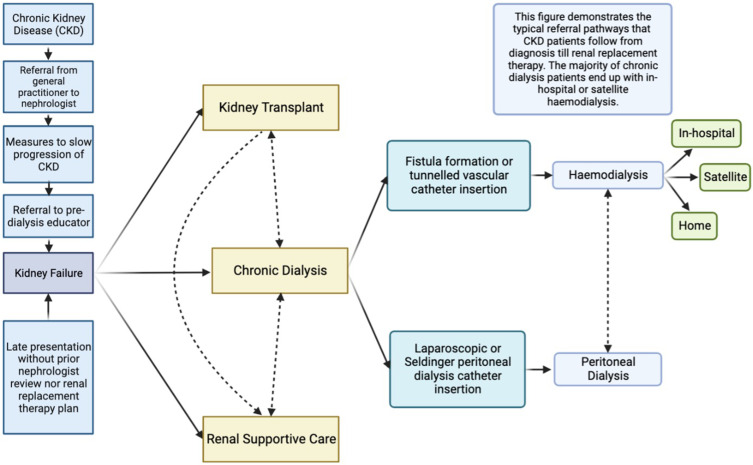
Figure 2.
This figure demonstrates the standard clinical pathways for kidney failure patients in the Western Renal Service. The ideal pathway is early referral from the general practitioner to a nephrologist for pre-dialysis medical care (eg treatment with ACE/ARB inhibitors, SGTL2 inhibitors and other measures) and assessment by the pre-dialysis educator to provide education and determine the optimal renal replacement plan with a preference for encouraging home-based treatments. Planning for dialysis involves surgical referral for either the creation of a fistula for haemodialysis (including Doppler vascular mapping) or consideration of insertion of a peritoneal dialysis catheter (either by laparoscopy or the Seldinger method). Recently, there has been a marked increase in patients who present with kidney failure without a prior plan who often require insertion of a tunnelled vascular catheter for acute start haemodialysis. Additionally, these patients can commence acute dialysis through peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion using the Seldinger method. Once established on chronic dialysis, patients undergo peritoneal dialysis; or haemodialysis either in-hospital, at a satellite centre or at home. Other management pathways include kidney transplantation or renal supportive care, and importantly patients can transition between these options at any time.