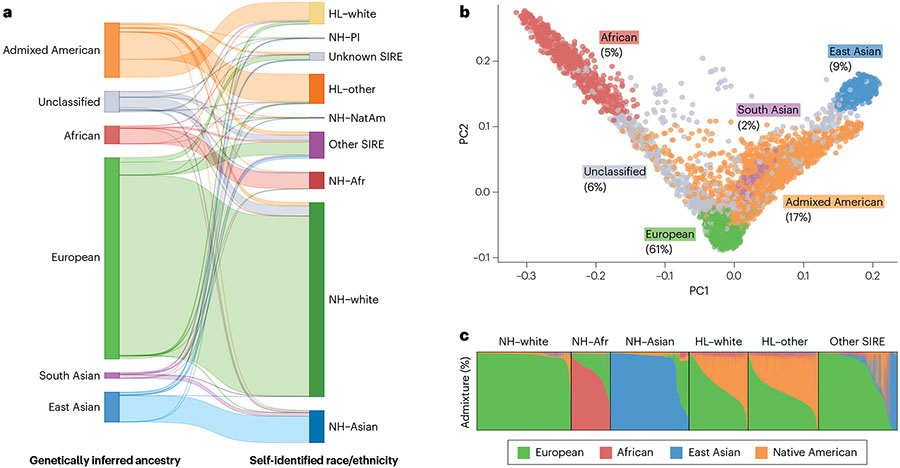
Fig. 1 ∣. Complex genetic ancestries and admixture using data from UCLA-ATLAS.
a, Comparison between genetically inferred ancestry and self-identified race and ethnicity (SIRE): Hispanic/Latino (HL), non-Hispanic/Latino (NH), Pacific Islander (PI), Native American (NatAm) and African/African American (Afr). Genetically inferred ancestry labels are assigned based on proximity to 1000 Genomes reference populations in principal component (PC) space using the k-nearest neighbour algorithm. SIRE is a composite label based on separate entries in the ‘Race’ and ‘Ethnicity’ fields extracted from medical records. b, First two PCs of the genetic data. Each dot represents an individual, with colours corresponding to their assigned genetically inferred ancestry cluster. A non-trivial percentage of individuals could not be categorized into a ‘homogeneous’ or ‘continental’ population. c, Unsupervised clustering of the genetic data. Each column represents the proportion of the global genetic ancestry of an individual with respect to 1000 Genomes reference populations.