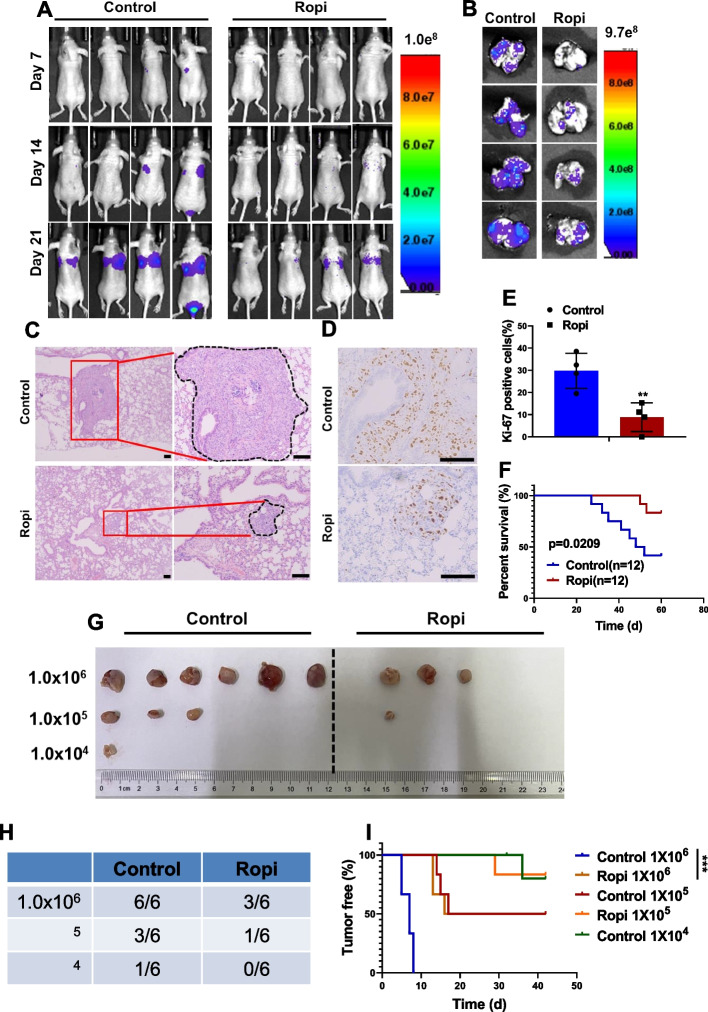
Fig. 2.
Effects of ropivacaine on CSC-like phenotypes of breast cancer cells in vivo. A Bioluminescence images of the metastatic burden of ropivacaine (40 μmol/kg, intraperitoneal injection, once every other day)- or negative control-treated mice at the indicated days after injection with MDA-MB-231 cells intravenously (n = 4). B-C Bioluminescence images (B) and H&E staining (C) of lungs from ropivacaine- or negative control-treated mice intravenously injected with MDA-MB-231 cells (scale bar = 100 μm) (n = 4). D-E Ki-67 staining of lung sections from ropivacaine- or negative control-treated mice intravenously injected with MDA-MB-231 cells (scale bar = 100 μm) (n = 4). F Survival curve of mice intravenously injected with MDA-MB-231 cells and treated with ropivacaine or negative control (n = 12). G-H The incidence of tumors in mice injected with different numbers of MDA-MB-231 cells and treated with ropivacaine or negative control (n = 6). I The tumor-free survival curves of the mice that were inoculated with different numbers of MDA-MB-231 cells with and without ropivacaine treatment (n = 6). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (log-rank test in F and I, others unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test)