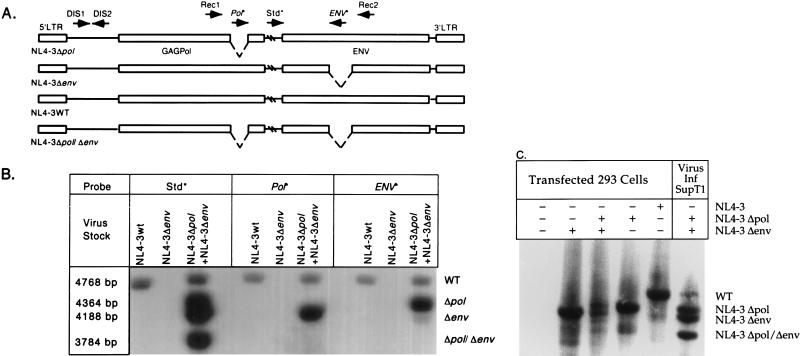
FIG. 3.
(A) Recombination between heterologous RNA during replication results in four proviral forms, the two parental forms, NL4-3Δpol and NL4-3Δenv, and two recombinant forms, wild-type NL4-3 (NL4-3WT) and NL4-3Δpol/Δenv. Arrows denote oligonucleotides used for PCR amplification (Rec1, Rec2, DIS1, and DIS2) and hybridization (Std*, Pol*, and ENV*) and the direction of sequence complementarity. Oligonucleotides marked with asterisks are probes for detecting PCR products. Hatch marks denote unrepresented sequences in HIV-1. Long terminal repeat (LTR) and structural genes are shown. (B) Provirus resulting from a single-cycle infection of SupT1 cells. Wild-type NL4-3 DIS (CG) and virus generated by cotransfection of NL4-3Δpol DIS (CG) and NL4-3Δenv DIS (CG) were used to infect SupT1 cells. Lysates of infected cells were amplified with primers Rec1 and Rec2, and proviral sequences were identified by hybridization with Std*, Pol*, and ENV* probes. Molecular weights of the PCR products confirm expected recombination products. (C) DNA recombination during virus production. Hirt supernatants from 293 cells transfected with no DNA, pNL4-3Δenv DIS (CG), pNL4-3Δenv DIS (CG) and NL4-3Δpol DIS (CG), NL4-3Δpol DIS (CG), or NL4-3 DIS (CG) were amplified with primers Rec1 and Rec2, and proviral sequences were identified by hybridization with the Std* probe. Lysate of SupT1 cells infected (Inf) with virus generated by cotransfection of NL4-3Δpol DIS (CG) and NL4-3Δenv DIS (CG) was amplified as a control. WT, wild type.