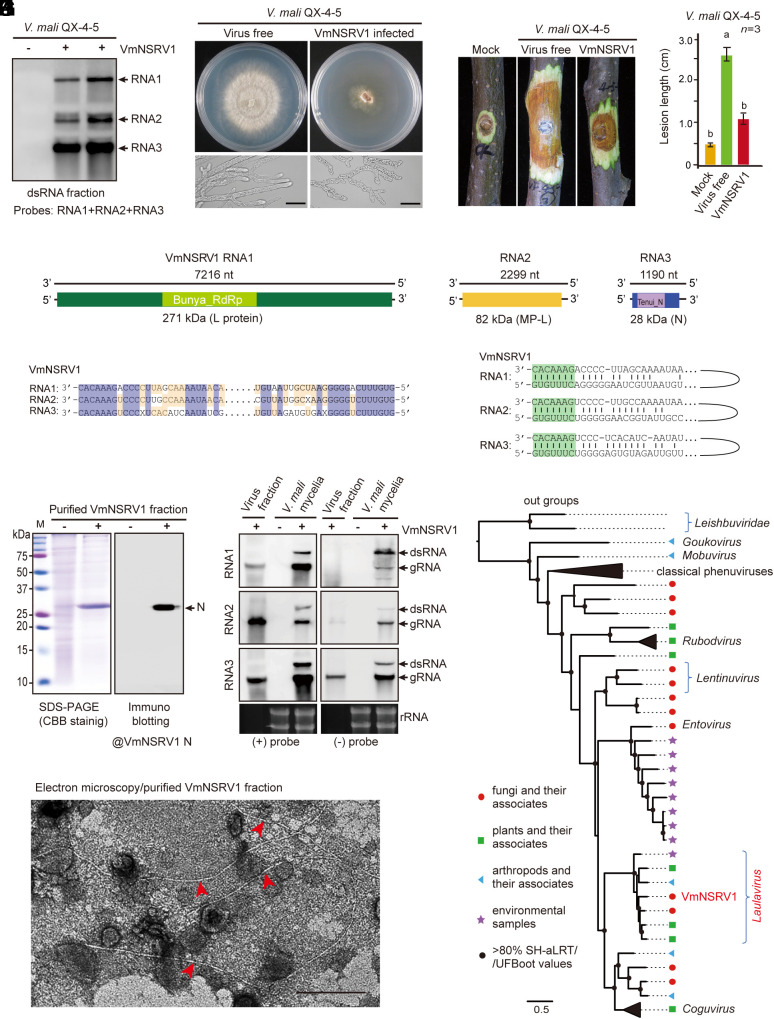
Fig. 1.
Identification of a hypovirulence-inducing negative-strand RNA virus from V. mali. (A) Detection of three RNA segments corresponding to the RNA1, 2, and 3 genomes of VmNSRV1 in a V. mali strain by RNA blotting with dsRNA fractions. (B) Phenotypic growth and mycelial morphology of a V. mali strain (VmNSRV1-free and -infected, QX-4-5) on PDA medium. The fungi were photographed at 3 d after culturing. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (C) Virulence assay of the V. mali (QX-4-5) strain on apple twigs. Fungal disease lesions (peeled twigs) were photographed at 5 d after inoculation. (D) Measurement of fungal disease lesions observed in the experiment described in (C). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). (E) A schematic genome structure of VmNSRV1. Black lines represent negative-strand genomic RNAs. Colored boxes represent open reading frames (ORFs) encoded by positive-strand genomic RNAs. The estimated molecular weight of each encoded protein (L[RdRp], MP-L, and N) is indicated. The relative position of conserved domains in the encoded RdRp and N proteins is presented (small colored boxes). (F) Sequence similarities of the 5′- and 3′-terminal regions of VmNSRV1 RNA1, 2, and 3 segments. (G) Sequence complementarity of the 5′- and 3′-terminal regions of each VmNSRV1 RNA1, 2, and 3 segment. (H) SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analyses of the protein associated with VmNSRV1 purified fractions. Immunoblotting was carried out using an antibody specific to the VmNSRV1 N protein. (I) Electron microscopy of a VmNSRV1 purified fraction from a virus-infected V. mali (QX-4-5) strain. Red arrowheads mark the potential VmNSRV1 particles. (Scale bar, 200 nm.) (J) Detection of positive- and negative-strand RNA of VmNSRV1 in purified virus fraction and mycelia of a virus-infected V. mali (QX-4-5) strain by RNA blotting. (K) Phylogenetic relationships of VmNSRV1 with phenuiviruses or other selected phenui-like viruses. The maximum likelihood tree was based on multiple sequence alignment of the RNA1-encoded L protein (RdRp). For the virus names and details of the tree, see SI Appendix, Fig. S6 and its legend.