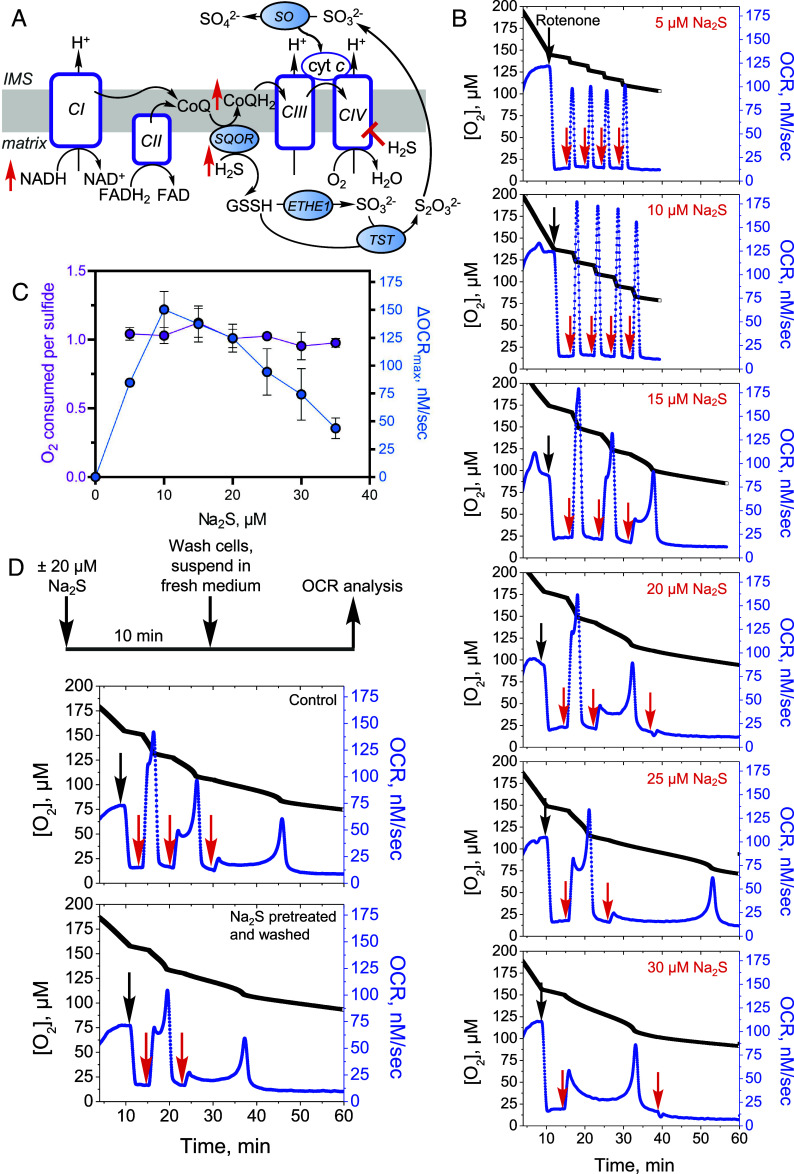
Fig. 1.
Effect of repeated sulfide exposure on ETC flux. (A) Sulfide inhibition of complex IV (CIV) causes electron acceptor insufficiency in the ETC due to a predicted build-up of NADH, CoQH2, and reduced cytochrome c (cyt c). IMS is intermembrane space, ETHE1 is persulfide dioxygenase, TST is thiosulfate sulfur transferase, and SO is sulfite oxidase. (B) Rotenone (0.5 µM)-treated HT29 cells exposed to low sulfide (5 to 10 µM) showed sharp increases in OCR with each aliquot of Na2S. At higher Na2S concentrations (15 to 30 µM), complex kinetics were observed. (C) Replotting the data in B as described under Methods showed a bell-shaped dependence of OCR on sulfide dose and an O2:sulfide ratio of 1.0 ± 0.1 between 5 and 35 µM Na2S. The data are representative of at least four independent experiments and represent the mean ± SD. (D) Experimental setup for removing residual sulfide and secreted oxidation products (Top). Washing did not impact the persistence of Na2S-triggered OCR (Bottom). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Black and red arrows indicate when rotenone and sulfide, respectively, were added.