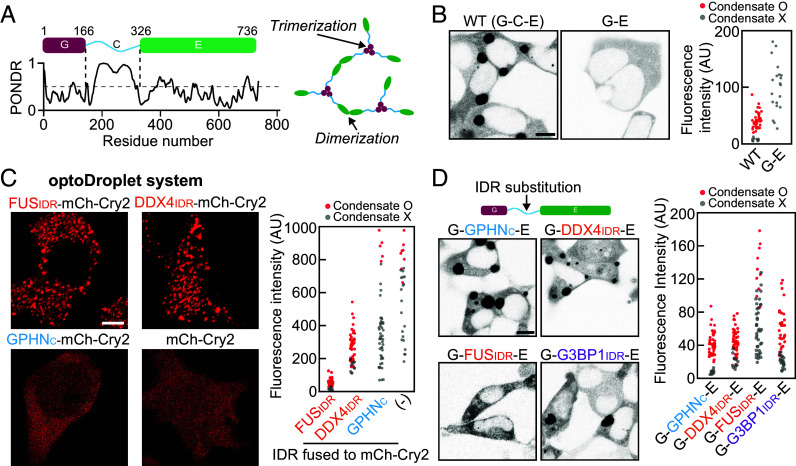
Fig. 2.
The role of the C domain in gephyrin phase separation. (A) (Left) Schematic of the domain organization of gephyrin. PONDR, prediction of intrinsic disorder. (Right) Gephyrin G and E domains undergo homotrimerization and dimerization, respectively. (B) (Left) Fluorescence images of EGFP-tagged gephyrin WT and gephyrin G-E in HEK293T cells. (Scale bar, 8 μm.) (Right) Cytosolic fluorescence intensities of HEK293T cells expressing gephyrin WT or G-E. (C) (Left) Fluorescence images of various optoDroplet constructs in HEK293T cells after activation of identical blue-light conditions. (Scale bar, 6 μm.) (Right) Cytosolic fluorescence intensities of HEK293T cells expressing different optoDroplet constructs. (D) (Left) Fluorescence images of EGFP-tagged gephyrin variants with different IDR substitutions. (Scale bar, 8 μm.) (Right) Cytosolic fluorescence intensities of HEK293T cells expressing gephyrin variants with different IDR substitution.