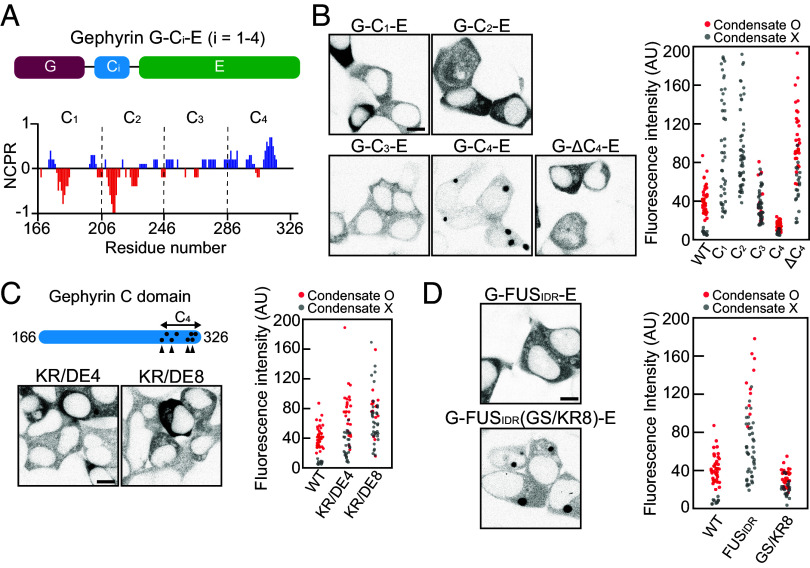
Fig. 3.
The positive charges near the C-terminal end of the C domain are important for phase separation. (A) Schematic of gephyrin variants with C-domain truncation. Net charge per residue plot of the gephyrin C domain, calculated with a sliding window of 5 residues. (B) (Left) Fluorescence images of EGFP-tagged gephyrin variants with different C-domain truncation or C4 deletion in HEK293T cells. (Scale bar, 8 μm.) (Right) Cytosolic fluorescence intensity of HEK293T cells expressing gephyrin WT or variants with different C-domain truncations or C4 deletion. (C) (Top Left) Schematic of gephyrin variants with positively charged residues mutated into negatively charged ones (KR/DE4 and KR/DE8). Dots indicate positively charged residues in the C4 subregion mutated in KR/DE8, and arrowheads denote the locations of mutated residues in both KR/DE4 and KR/DE8. (Bottom Left) Fluorescence images of gephyrin variants, KR/DE4 and KR/DE8 in HEK293T cells. (Scale bar, 8 μm.) (Right) Cytosolic fluorescence intensity of HEK293T cells expressing gephyrin WT or variants. (D) (Left) Fluorescence images of EGFP-tagged G-FUSIDR-E and G-FUSIDR(GS/KR8)-E in HEK293T cells. (Scale bar, 8 μm.) (Right) Cytosolic fluorescence intensity of HEK293T cells expressing gephyrin WT or variants.