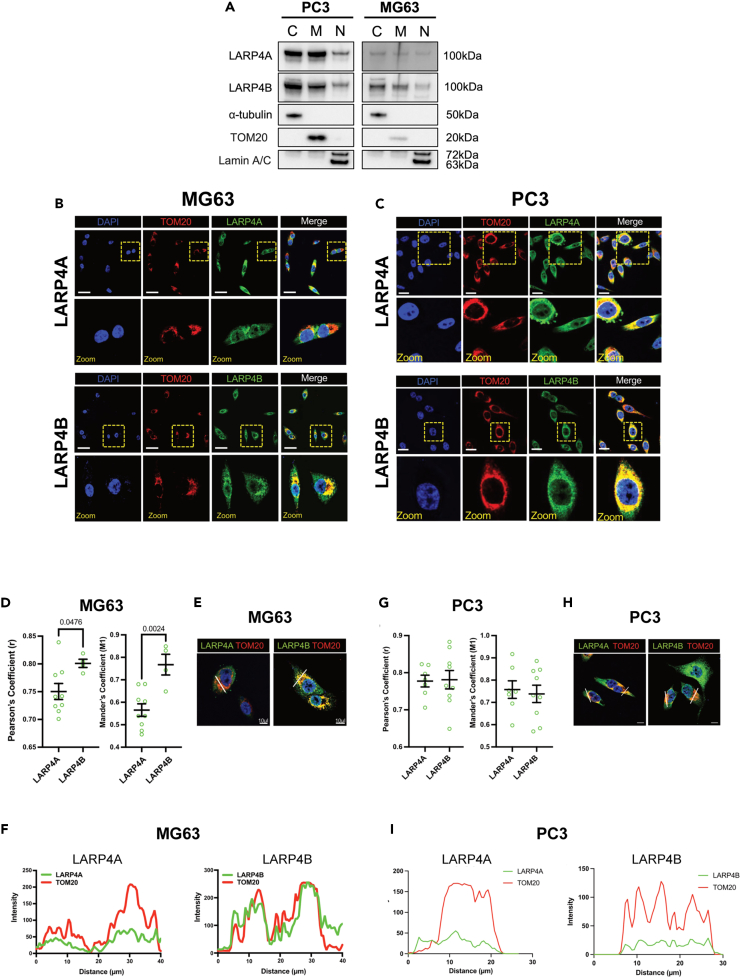
Figure 7.
Expression and localization of LARP4A and LARP4B in mitochondria
(A) Western blot analysis of endogenous LARP4A and LARP4B in PC3 and MG63 cells following the fractionation of cytoplasm (C), mitochondria (M) and nuclei (N). α-tubulin, TOM20, and Lamin A/C are used as respective controls to determine fraction purities.
(B and C) Immunofluorescence detection of TOM20 in (B) PC3 and (C) MG63 cells and co-localization with LARP4A and LARP4B proteins with DAPI counterstain. Scale bars, 25μm. Areas in yellow squares are depicted at higher magnification in lower panels.
(D) Pearson’s and Mander’s coefficient analyses showing a higher degree of LARP4B/TOM20 co-localization compared with LARP4A/TOM20 in MG63 cells. The data represent the mean ± SEM, n = 6 from three independent experiments. p values are indicated.
(E and F) Fluorescent intensity line plot profiling demonstrating the co-localization of LARP4A and LARP4B with the TOM20 mitochondrial marker in MG63 cells. White lines in (E) depict the areas used for LARP4A/TOM20 and LARP4B/TOM20 line plot analyses as indicated in (F). Scale bars in (E), 10μm.
(G) Pearson’s and Mander’s coefficient analyses showing a similar degree of LARP4B/TOM20 co-localization compared with LARP4A/TOM20 in PC3 cells. The data represent the mean ± SEM, n = 6 from three independent experiments. p values are indicated.
(H and I) Fluorescent intensity line plot profiling demonstrating the co-localization of LARP4A and LARP4B with the TOM20 mitochondrial marker in PC3 cells. White lines in (H) depict the areas used for LARP4A/TOM20 and LARP4B/TOM20 line plot analyses as indicated in (I). Scale bars in (H), 10μm. See also Figure S7.