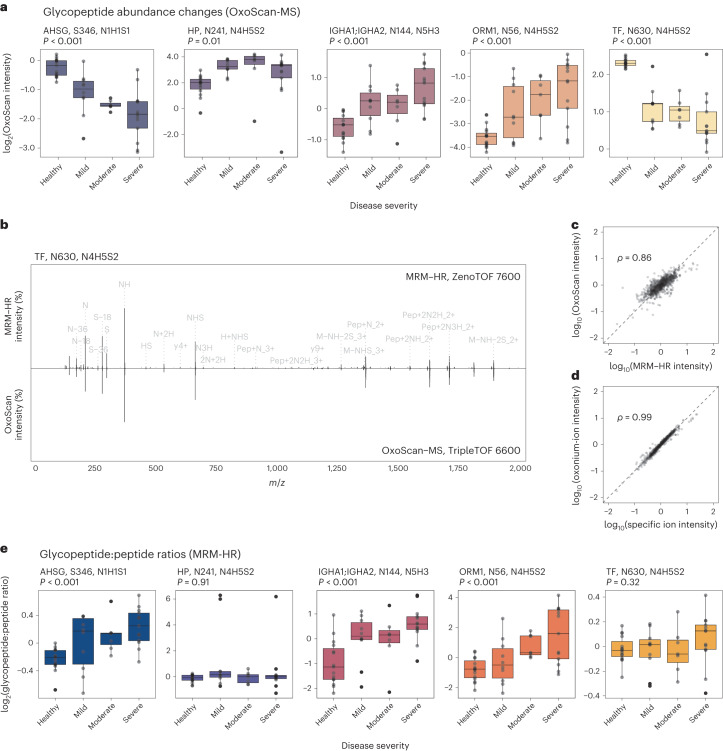
Fig. 5. OxoScan-MS identifies differential abundance of intact glycopeptides with COVID-19 disease severity.
Detection of site-specific regulation in the plasma glycoproteome of SARS-CoV-2 patients and healthy controls, first by OxoScan-MS and separately validated by MRM-HR in a second laboratory. a, OxoScan-MS intensities for five glycopeptides across a clinical COVID-19 cohort, demonstrating robust differential abundance of glycopeptides with disease severity. Significance was calculated using the Kendall–Tau test for the Theil–Sen trend estimator and adjusted for multiple testing according to the Benjamini–Hochberg FDR approach99. Boxplots display 25th, 50th (median) and 75th percentiles; whiskers display upper/lower limits of data. b, Representative back-to-back spectra from MRM-HR and OxoScan-MS fragment spectra, showing high overlap between identified fragment ions across different instruments and acquisition methods. Annotated peaks are shared between both MRM-HR and OxoScan-MS. Peak labelling was only displayed above a minimum base peak intensity of 2% for clarity. c, Correlation of OxoScan-MS intensities and MRM-HR intensities for validated glycopeptide targets show excellent agreement. The Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated using all validated glycopeptide features (n = 17). d, Oxonium ion intensities and glycopeptide-specific ions (Y-type) show excellent agreement. Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated using the sum intensities of oxonium ions (m/z 138.055, 186.076, 204.087, 274.092, 292.103, 366.139, 657.235) and the 5 highest intensity specific ions identified in Skyline for all validated glycopeptide features (n = 17). e, Boxplots showing intensity ratios of each glycopeptide, normalized to adjacent non-glycosylated peptides from the same protein measured in the same MRM-HR run. At least 2 non-glycosylated precursors were used for normalization in each case (see Methods). For IGHA1;IGHA2, peptides shared between both subclasses were used for normalization, although no significant difference was seen between subclasses (Extended Data Fig. 6b). Significance and boxplot information as in a.