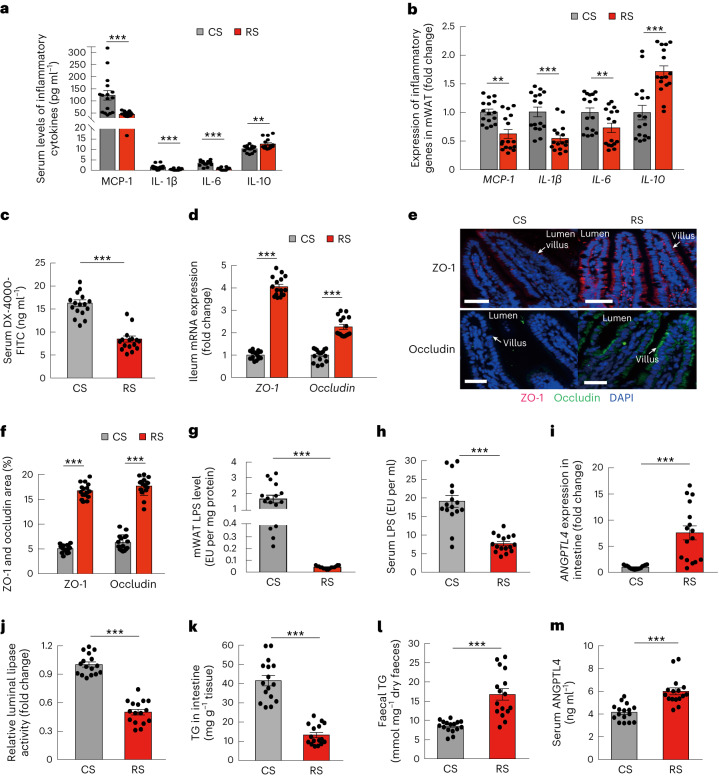
Fig. 5. RS-influenced gut microbiota restores gut barrier and reduces lipid absorption.
Mice were grouped and treated as in Fig. 4 (n = 16 per group). a, Serum levels of inflammatory cytokines in mice colonized with microbiota from RS or CS donors. b, The expression of inflammatory genes in mWAT and in mice colonized with microbiota from RS or CS donors. c, Gut permeability in vivo. d, The expression of ZO-1 and occludin in the ileum. e, The localizations and levels of ZO-1 (red) and occludin (green) in intestinal villus were visualized by immunofluorescence and counterstaining with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Representative images of each group are shown (scale bar, 50 µm). f, Quantitative analysis of the positive stained area of ZO-1 and occludin was performed by ImageJ software and calculated as the percentage of total lesion area. g,h, LPS levels in mWAT and in circulation (serum). i, Expression levels of ANGPTL4 in the ileum. j, Relative intestinal luminal lipase activity. k, TG levels in the ileum. l, Faecal TG levels. m, Serum ANGPTL4 levels. Data were reproduced in three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. Significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (normally distributed) or nonparametric two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test (non-normally distributed). **P = 0.005 (a) and 0.001 and 0.010 (b), ***P < 0.001.