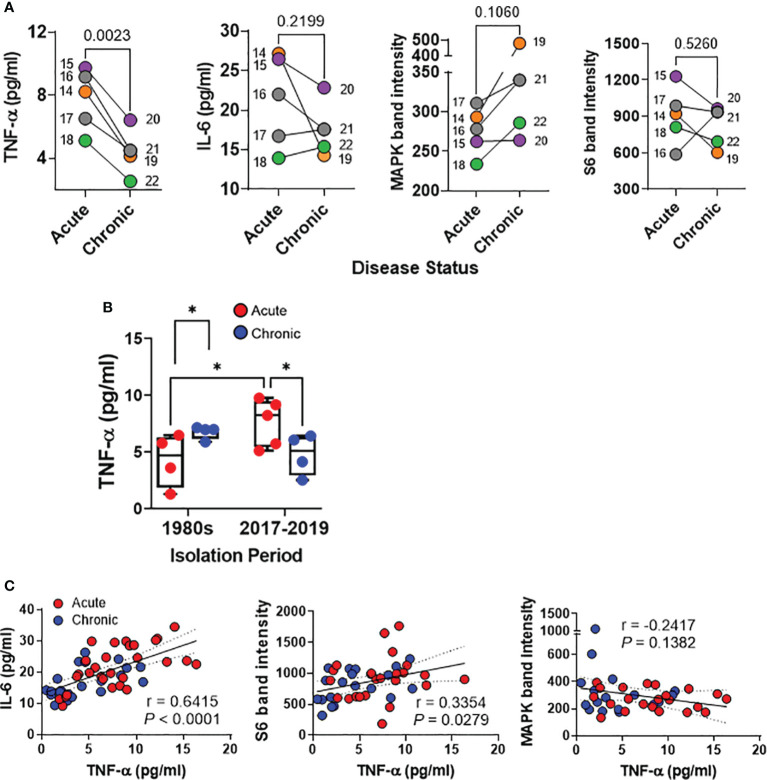
Figure 6.
Detection of host responses after exposure of the HODGM model to S. Typhi strains with epidemiological linkage isolated between 2017and 2019. Epithelial cells from the HODGM model were exposed to 9 S. Typhi strains isolated from acutely infected (n=5) or chronically (n=4) infected individuals. HODGM models cultured with media only were used as negative controls. (A) After 5 hours, the supernatants were collected from the upper chambers of the HODGM model to measure IL-6 and TNF-α cytokines. Cells were also harvested, lysed, and phosphorylation of S6 and MAPK, were detected by western blot. Data are representative of the net responses observed in 2 independent experiments. Net responses were calculated by subtracting the responses of the controls (media) from those in cells exposed to S. Typhi. Each dot is the average of 2 experiments with 2-3 independent replicates. Colors denote the strain linkage: ( ) 14 & 19, (
) 14 & 19, ( ) 15 & 20, (
) 15 & 20, ( ) 16-17 & 21, (
) 16-17 & 21, ( ) 18 & 22. Two-tailed paired t-tests were used to account for the strain linkage. (B) Production of TNF-a by the HODGM model exposed to 17 S. Typhi strains isolated in two distinct periods, 1980s from 4 acutely (
) 18 & 22. Two-tailed paired t-tests were used to account for the strain linkage. (B) Production of TNF-a by the HODGM model exposed to 17 S. Typhi strains isolated in two distinct periods, 1980s from 4 acutely ( ), and 4 chronically (
), and 4 chronically ( ) infected individuals and between 2017 and 2019 from 5 acutely (
) infected individuals and between 2017 and 2019 from 5 acutely ( ), and 4 chronically (
), and 4 chronically ( ) infected individuals. Mixed-effects model was used to compare multiple groups. The data are representative of 4 experiments with 2 independent replicates. (C) Correlation between TNF-a levels and IL-6, S6, and MAPK after exposure to S. Typhi strains isolated from acutely (
) infected individuals. Mixed-effects model was used to compare multiple groups. The data are representative of 4 experiments with 2 independent replicates. (C) Correlation between TNF-a levels and IL-6, S6, and MAPK after exposure to S. Typhi strains isolated from acutely ( ) and chronically (
) and chronically ( ) infected individuals. The data are representative of 2 experiments with 2-3 independent replicates The solid line represents the trendline. Dashed lines represent 95% confidence intervals. Shown are the coefficient of determination “r” and the “P” value. Correlations were determined using the two-sided Pearson Product Moment tests. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
) infected individuals. The data are representative of 2 experiments with 2-3 independent replicates The solid line represents the trendline. Dashed lines represent 95% confidence intervals. Shown are the coefficient of determination “r” and the “P” value. Correlations were determined using the two-sided Pearson Product Moment tests. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.