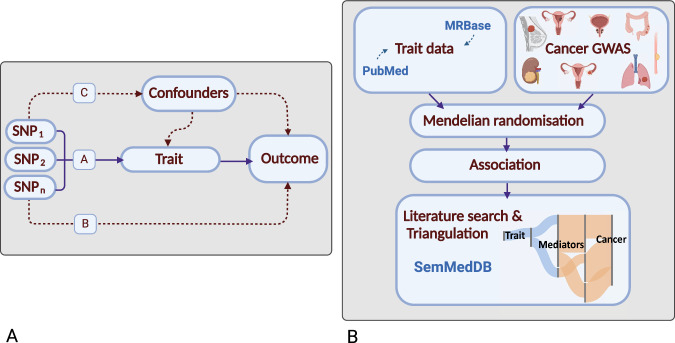
Fig. 1. Principles of Mendelian randomisation (MR) and study overview.
A Assumptions in MR that need to be satisfied to derive unbiased causal effect estimates. Dashed lines represent direct causal and potential pleiotropic effects that would violate MR assumptions. A, indicates genetic variants used as IVs are strongly associated with the trait; B, indicates genetic variants only influence cancer risk through the trait; C, indicates genetic variants are not associated with any measured or unmeasured confounders of the trait-cancer relationship. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; B Study overview. Genetic variants serving as instruments for exposure traits under investigation were identified from MRBase or PubMed. GWAS data for the eight cancers was acquired and MR analysis was performed. Results were triangulated through literature mining to provide supporting evidence for potentially causal relationships. Created with BioRender.com. GWAS genome-wide association study.