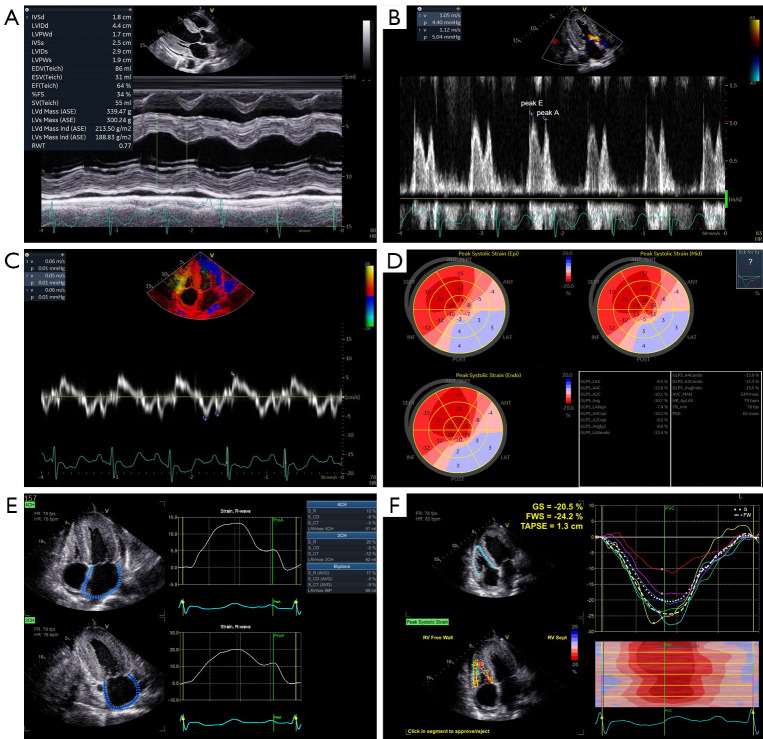
Figure 2.
Conventional and speckle tracking echocardiography in a 53-year-old male patient with light-chain cardiac amyloidosis and non-apical sparing. New York Heart Association stage was III, serum NT-proBNP was 1,519 pg/mL, and serum troponin I was 4.7 pg/mL. M-mode echocardiogram exhibited increased left ventricular wall and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction of 64% (A). Peak E wave velocity was 112 cm/s, peak A wave velocity was 105 cm/s, and E/A ratio was 1.07 on mitral inflow pulsed-wave Doppler recording (B). Septal mitral annular velocities e', a' and s were 6, 5 and 6 cm/s, respectively, and E/e’ ratio was 18.7 on tissue Doppler recording (C). (D) was a bull’s eye plot of left ventricular longitudinal strain. Global longitudinal strain was −10.7% and relative apical longitudinal strain was 0.87. (E) showed the results of biplane left atrial strain analysis, with left atrial reservoir strain of 17%, left atrial conduit strain of −8% and left atrial contraction strain of −9%. (F) showed the results of right ventricular strain analysis. Right ventricular global strain, free wall strain and tricuspid annular systolic plane excursion were −20.5%, −24.2% and 13 mm, respectively. IVSd, diastolic interventricular septum; LVIDd, diastolic left ventricular internal diameter; LVPWd, diastolic left ventricular posterior wall; IVSs, systolic interventricular septum; LVIDs, systolic left ventricular internal diameter; LVPWs, systolic left ventricular posterior wall; EDV(Teich), end-diastolic volume; ESV(Teich), end-systolic volume; EF(Teich), ejection fraction; FS, fractional shortening; SV(Teich), stroke volume; LVd Mass (ASE), diastolic left ventricular mass; LVs Mass (ASE), systolic left ventricular mass; LVd Mass Ind (ASE), diastolic left ventricular mass index; LVs Mass Ind (ASE), systolic left ventricular mass index; RWT, relative wall thickness; HR, heart rate; peak E, peak early diastolic mitral inflow velocity; peak A, peak late diastolic mitral inflow velocity; v, velocity; p, pressure gradient; epi, subepicardial layer; mid, mid layer; endo, subendocardial layer; SEPT, septum; ANT_SEPT, anteroseptum; ANT, anterior wall; LAT, lateral wall; POST, posterior wall; INF, inferior wall; GLPS_LAX, global longitudinal peak strain of apical long-axis view; GLPS_A4C, global longitudinal peak strain of apical four-chamber view; GLPS_A2C, global longitudinal peak strain of apical two-chamber; GLPS_Avg, average global longitudinal peak strain; AVC_AUTO, auto aortic valve closing time; HR_ApLAX, heart rate from apical long-axis view; bpm, beats per minute; FR min, minimal frame rate; fps, frames per second; PSD, peak strain dispersion; FR, frame rate; 4CH, four-chamber view; 2CH, two-chamber view; AVG, average; S_R, reservoir strain; S_CD, conduit strain; S_CT, contraction strain; LAVmax 2CH, maximum left atrial volume of two-chamber view; preA, defined as onset of the A-wave in the mitral inflow profile; GS, global strain; FWS, free wall strain; TAPSE, tricuspid annular systolic plane excursion; PVC, pulmonary valve closing time; G, global strain; FW, free wall strain; RV, right ventricular.