Fig. (1).
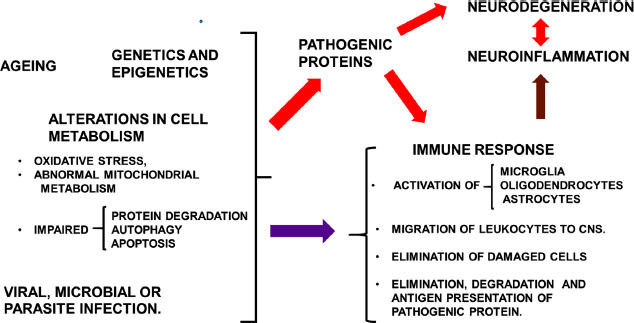
General overview of the interaction between neurodegenerative diseases, immune response, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. On the left side, ageing, genetic and epigenetic factors, and viral, microbial or parasite infections induce alterations in cell metabolism with impaired abnormal protein degradation, autophagy and apoptosis, and the secretion of pathogenic proteins (red arrow). Pathogenic proteins can induce neurodegeneration and immune response activation (red arrows). All the previous events can cause activation of the immune response (purple arrow). Local and/or peripheral immune response activation induces neuroinflammation (brown arrow), leading to neurodegeneration. Neural cell death also activates the immune response (red double arrows).
