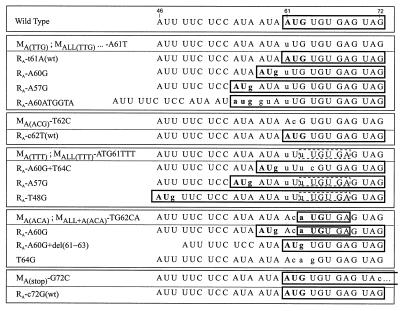
FIG. 5.
True and second-site reversions of sORF A generated in planta. Different types of sORF A mutations (designated on the left) and the corresponding reversions are grouped in panels. The coding sequences of the wild-type sORF A (in the uppermost panel) and the reverted sORF As are boxed. Lowercase letters indicate nucleotides that do not occur in the wild-type sequence. The mini-sORF created in place of sORF A by some mutations is also boxed (a dashed box shows the same mini-sORF which might be opened by the TTG codon). In mutant MA(stop) (in the bottom panel), sORF A extends for an additional 23 codons.