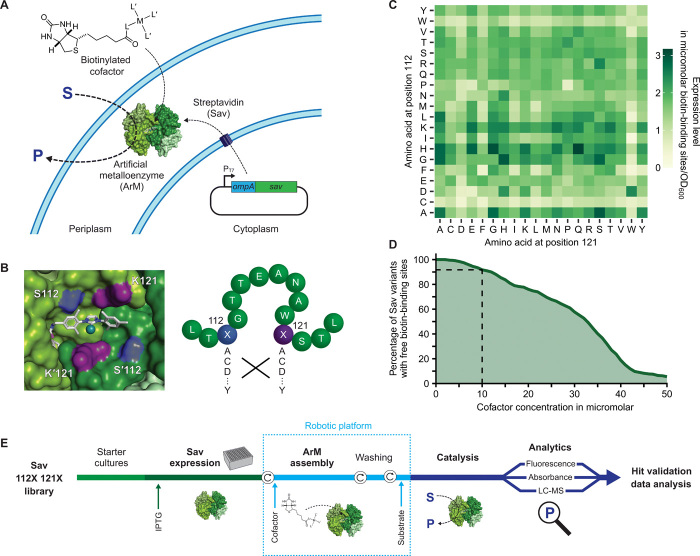
Fig. 1. Systematic screening of ArMs.
(A) Sav is secreted to the periplasm, where it binds an externally added biotinylated cofactor, which consists of a catalytic metal M and ligands L and L′, to afford an ArM. OmpA, periplasmic export signal from outer membrane protein A. (B) Left: Biotinylated metathesis cofactor embedded in the biotin-binding vestibule of homotetrameric Sav (Protein Data Bank 5IRA). Symmetry-related residues S112/S′112 (blue) and K121/K′121 (purple) are in the immediate vicinity of the cofactor and were mutated (right) to afford an Sav library of 400 amino acid combinations. (C) Expression level of periplasmic Sav mutants as determined in cell lysate using a fluorescence quenching assay (Methods) (41). Means of biological triplicates (n = 3) normalized to the OD600 of the cultures are displayed (see fig. S4 for SD). (D) Estimated percentage of Sav mutants with unoccupied biotin-binding sites as a function of the cofactor concentration added to the cell suspension (assuming 50% uptake into the periplasm). Ten micromolars was selected as maximum-permitted cofactor concentration for further experiments to ensure an excess of binding sites for >90% of Sav variants (dashed lines). (E) Overview of the screening workflow (see Results and Methods). Circular arrows represent centrifugation steps for buffer exchange.