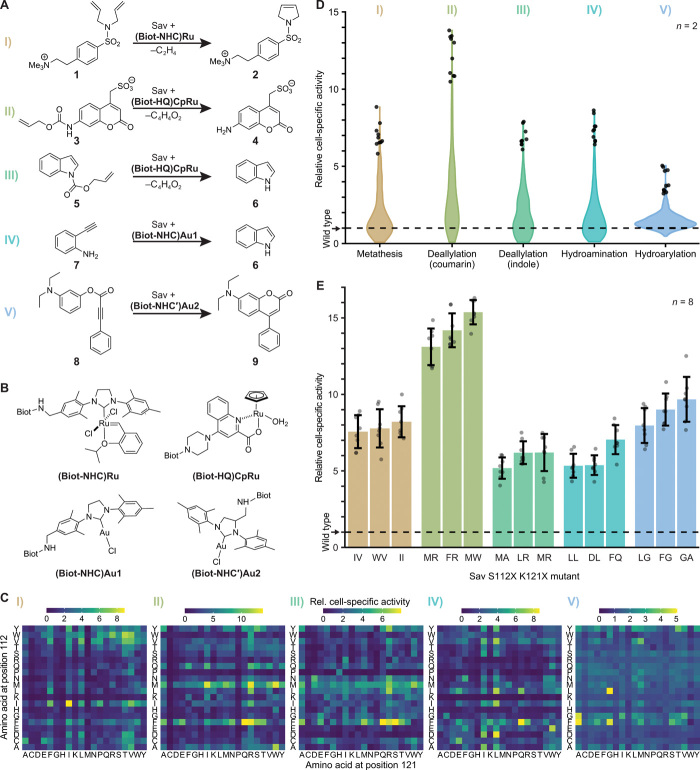
Fig. 2. Systematic screening for ArMs catalyzing diverse reactions.
(A) ArM-catalyzed reactions: I, ring-closing metathesis (RCM) with a diallyl-sulfonamide 1 yielding a 2,5-dihydro-pyrrole 2. II, Deallylation of allylcarbamate-protected coumarin 3 to the corresponding amino coumarin 4. III, Deallylation of allyl carbamate indole 5 to indole 6. IV, Hydroamination of 2-ethynylaniline 7 to indole 6. V, Hydroarylation of profluorophore 8 to afford amino coumarin 9. (B) Biotinylated cofactors used in this study. Biot: d-biotin. (C) Cell-specific activity of 400 ArMs mutated at Sav positions 112 and 121 normalized to the activity of wild-type Sav (S112 K121). The displayed activities are product concentrations after 20 hours of reaction (mean of biological duplicates; for SDs, refer to fig. S8). Note that the screenings for reactions II and V were performed using robotics. (D) Activity distribution in the Sav mutant library for the five ArM reactions. Violins comprise 400 double mutants with the 10 most active ArMs depicted as circles. (E) Validation of hits from the 400 mutant screens. Bars are mean activity of eight biological replicates with SD (error bars) and individual replicates (circles). Mutants are designated by the amino acids in positions 112 and 121.