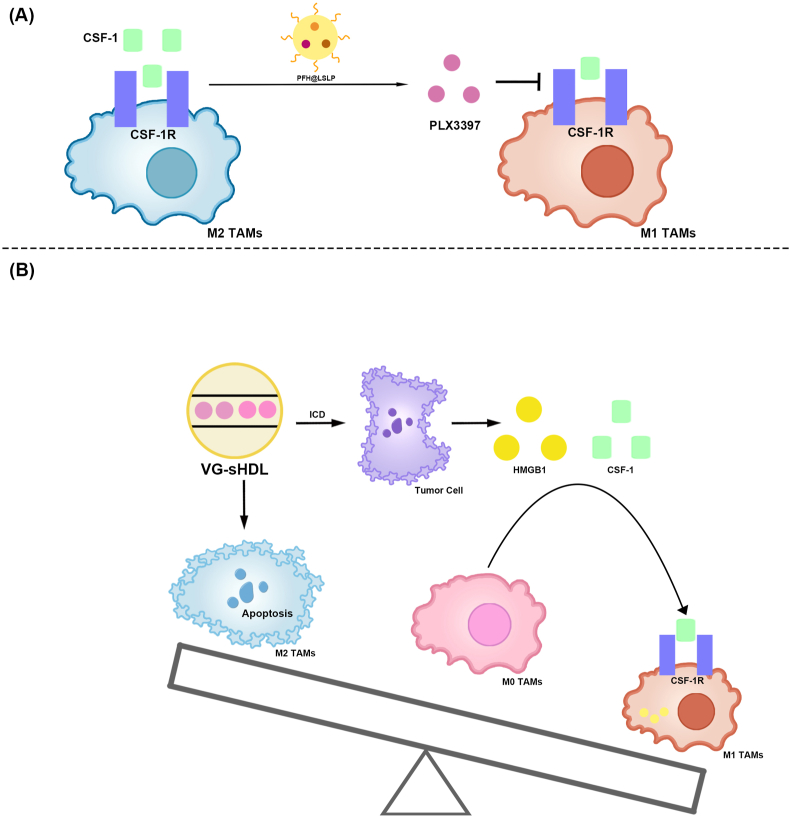
Fig. 10.
Nanomaterials modulating TAM polarization for the treatment of HCC via the CSF-1/CSF–1R signaling pathway.
(A) PFH@LSLP inhibits the CSF-1/CSF–1R signaling pathway by releasing PLX3397 blockade, which in turn promotes M2-type TAM polarization to M1.
(B) VG-sHDL targets HCC cells and M2-type TAMs, resulting in cell death. ICD released CSF-1 and HMGB1 from HCC cells and promoted monocyte differentiation into M1-type. VG-sHDL reduced the content of M2-type TAMs and increased the content of M1-type TAMs. TAMs, Tumor-associated macrophages; HCC, Hepatocellular carcinoma; CSF-1/CSF–1R, Colony stimulating factor-1/CSF-1 receptor; PFH@LSLP, An oxygensaturated perfluorohexane-cored liposome, with LFC131 peptides modifying on the surface to deliver sorafenib and PLX3397; VG-sHDL, Vadimezan and Gemcitabine-Synthetic high-density lipoproteins; ICD, Immunogenic cell death; CSF-1, Colony stimulating factor-1; High mobility group box-1 protein, HMGB1.