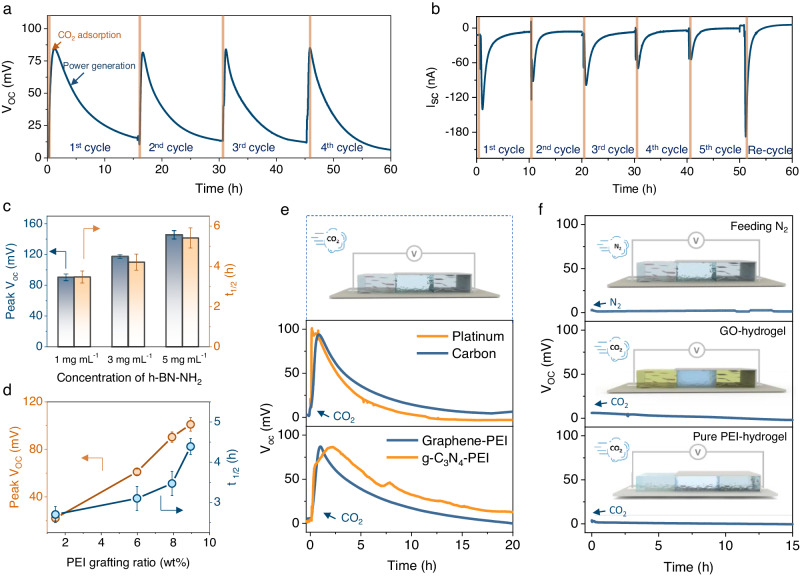
Fig. 2. CO2-induced electricity generation of NAH electricity generator and the effects of key factors on performance.
a Cyclic CO2 adsorption-induced open circuit voltage of NAH electricity generator. b Cyclic CO2 adsorption-induced short circuit current of NAH electricity generator. A pH-swing was applied to recover the power generation after the 5th cycle. The CO2 was fed into the testing box at a rate of 2.5 L min-1 for 3 min in each cycle for both VOC and ISC tests. c Electricity generation in terms of the peak VOC and half value time (t1/2) of the induced open circuit potential as a function of the concentration of the h-BN-NH2 nanosheets in agarose hydrogel. d Electricity generation in terms of the peak VOC and half value time (t1/2) of the induced open circuit potential as a function of the weight ratio of PEI functionalities on h-BN nanosheets. Error bars are standard deviations from three tests. e Electricity generation using carbon and platinum electrodes for electrical signals collection (middle panel), and Electricity generation using PEI functionalized graphene (Graphene-PEI) and PEI functionalized graphic carbon nitride (g-C3N4-PEI) (bottom panel). f Electricity generation in different control experiments: using N2 to substitute CO2 as the feed gas for the testing (top panel), replacing the h-BN nanosheets in the generator with graphene oxide nanosheet (middle panel) and pure PEI molecules (bottom panel).