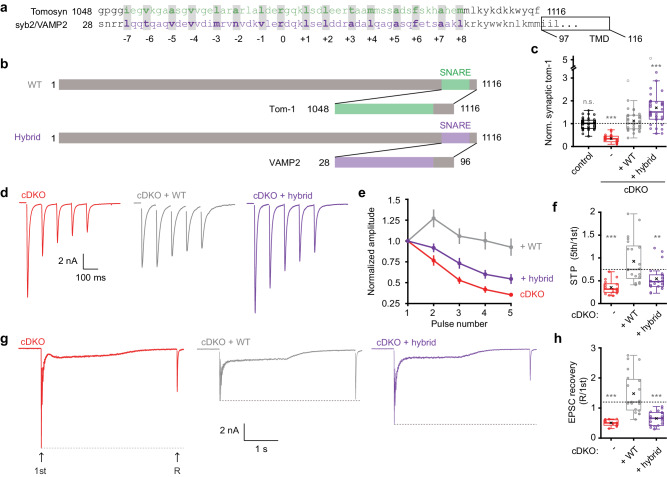
Fig. 3. A tomosyn-VAMP2 hybrid fails to fully restore tomosyns’ inhibitory function.
a Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the syb2/VAMP2 and tomosyn R-SNARE motifs. TMD = transmembrane domain. b Schematic representation of WT tomosyn-1m and the hybrid mutant, in which we replaced the C-terminus of tomosyn with the corresponding region in VAMP2. Numbers correspond to amino acids. c Synaptic tomosyn-1 expression from immunostainings, normalized to control within each neuronal culture. Control n = 35/3, cDKO n = 30/3, +WT n = 33/3, +Hybrid n = 35/3; p = 0.3902 (control vs +WT); ***p < 0.0001 (cDKO vs +WT), ***p = 0.0002 (+hybrid vs +WT). d–f Analysis of short-term plasticity (STP) by stimulating neurons with five pulses at 10 Hz. cDKO n = 17/4, +WT n = 21/4, +Hybrid n = 21/4. d Example traces. e Amplitudes were normalized to the first pulse of the train. f STP quantified by the ratio of the fifth pulse over the first pulse; ***p < 0.0001 (cDKO vs +WT), **p = 0.0023 (+hybrid vs +WT). g, h Recovery of the first EPSC amplitude (1st) was tested by high-frequency stimulation (80 pulses at 40 Hz) followed by a recovery pulse after 2 s (R). cDKO n = 14/4, + WT n = 20/4, +Hybrid n = 18/4. g Example traces. h The amplitude of the recovery pulse was divided by the first amplitude of the train; ***p < 0.0001 (cDKO vs +WT), ***p < 0.0001 (+hybrid vs +WT). N = cells/independent cultures. In (c, f, h), boxplots display median (center), upper and lower quartiles (box bounds), and whiskers to the last datapoint within 1.5x interquartile range. In (e), data are presented as mean ± SEM. A one-way ANOVA tested the significance of adding experimental group as a predictor, see Supplementary Table 1. For post-hoc comparison to + WT group, p value thresholds (*<0.05; **<0.01;***<0.001) were adjusted with a Bonferroni correction (α/number of tests). Abbreviations: TMD (transmembrane domain), n.s. (not significant). See also Supplementary Fig. 7. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.