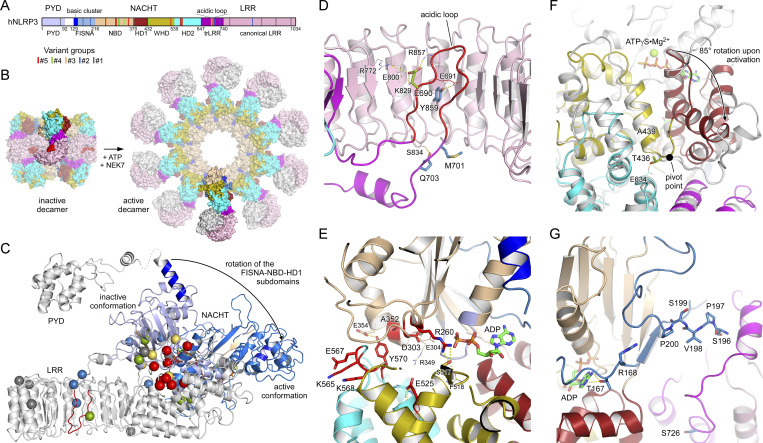
Figure 6.
Localization of disease mutant sites in the structure of human NLRP3. (A) Bar diagram showing the domain architecture of NLRP3 with the mutant sites of the five variant groups indicated. (B) Display of the inactive spherical NLRP3-ADP decamer (7PZC) (Hochheiser et al., 2022) and the active radial NLRP3-ATP decamer bound to NEK7 (in gray) (8EJ4) (Xiao et al., 2023). (C) The conformational transition from the inactive to the active state in NLRP3 involves an 85° rotation of the FISNA-NBD-HD1 subdomains in the NACHT relative to the remainder. The missense mutations of the five variant groups are highlighted as spheres in the inactive conformation. (D) Close-up of residues E690, M701, and Q703 in the loop section of the transition LRR and Y859 in the concave side of the LRR. (E) Localization of the constitutively active group#5 mutant sites in the NACHT domain of NLRP3. (F) Residues T436 and A439 are at the pivot point of the FISNA-NBD-HD1 rotation. The active state (8EJ4) is shown in gray relative to the colored inactive state (7PZC). (G) Variant group#2 residues R168 and V198 in the FISNA domain and S726 in the trLRR are located in variable regions of NLRP3.