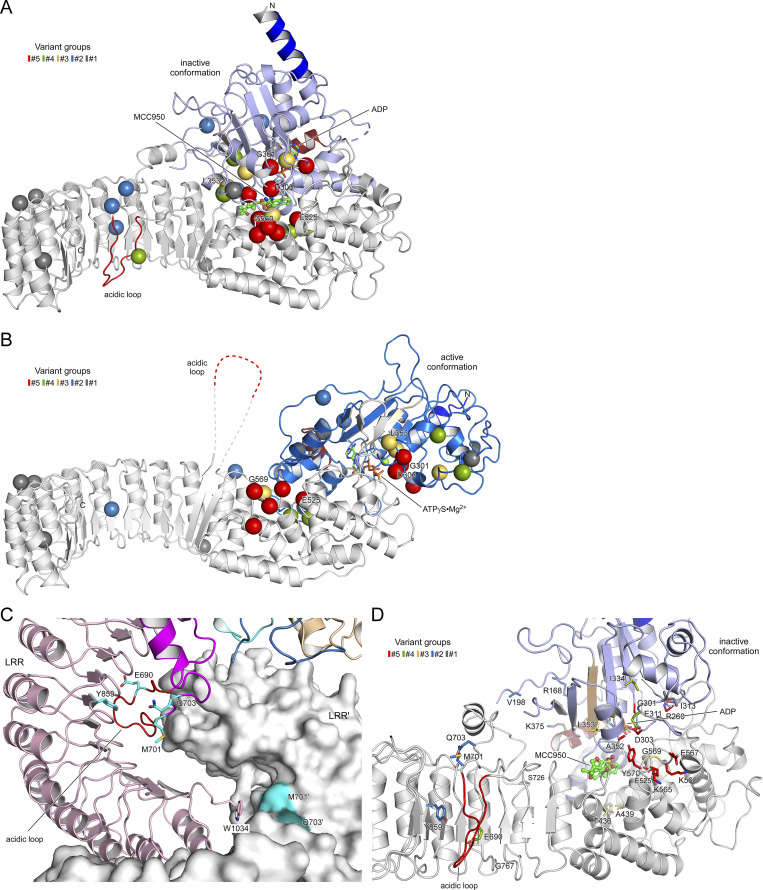
Figure S7.
Details of the disease-causing mutant sites in NLRP3 and MCC950 inhibition. (A) Localization of gain-of-function mutations in the MCC950-inhibited state of human NLRP3 (7PZC), color-coded according to variant groups. The five mutant positions that are not responsive to MCC950 treatment, G301D, E303H, L353P, E525K, and G569R, are labeled. (B) Localization of gain-of-function mutations in the adenosine triphosphate-bound active state of human NLRP3 (8EJ4). (C) The three gain-of-function mutations in the acidic loop of NLRP3, E690, M701, and Q703, are in the dimer interface of the interlaced LRRs, while Y859 in the concave surface of the LRR interacts with the acidic loop. (D) MCC950 is in the center of the NACHT and LRR domains in proximity to many disease-causing mutations.