Figure 8.
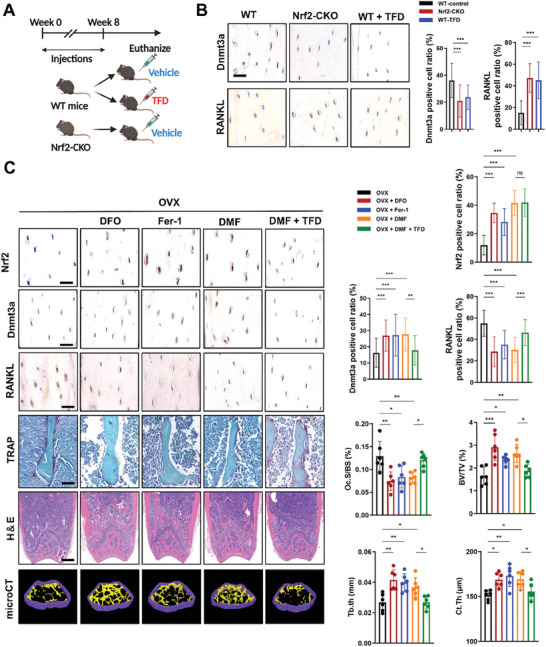
Targeting Nrf2 can effectively inhibit Dnmt3a‐mediated RANKL overexpression, thereby improving bone loss. A) Schematic showing the experimental protocol for 8 weeks of TFD injections in mice. B) IHC for Dnmt3a and Immunofluorescence staining for RANKL. Representative images are shown. SFI treatment inhibited the Dnmt3a expression while enhanced the RANKL expression in osteocytes of mice (Five randomly selected viewing fields were evaluated per section, and 6 mice were evaluated per group). Scale bar: 20 µm. C) Representative image of Nrf2, Dnmt3a, and RANKL IHC staining, TRAP staining, HE staining, and microCT 3D reconstruction are shown. Iron chelator (DFO), anti‐ferroptosis treatment (Fer‐1), and Nrf2 agonist (DMF) could to some extent suppress the expression of RANKL in osteocytes, thus inhibiting bone loss mediated by osteoclasts. TFD significantly inhibited the protective effect of DMF. Nrf2, Dnmt3a, and RANKL IHC staining Scale bar: 20 µm. HE staining Scale bar: 20 µm. TRAP staining Scale bar: 20 µm. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Two‐tailed paired t test or ANOVA with post‐hoc Tukey–Kramer test.
