Fig. 3.
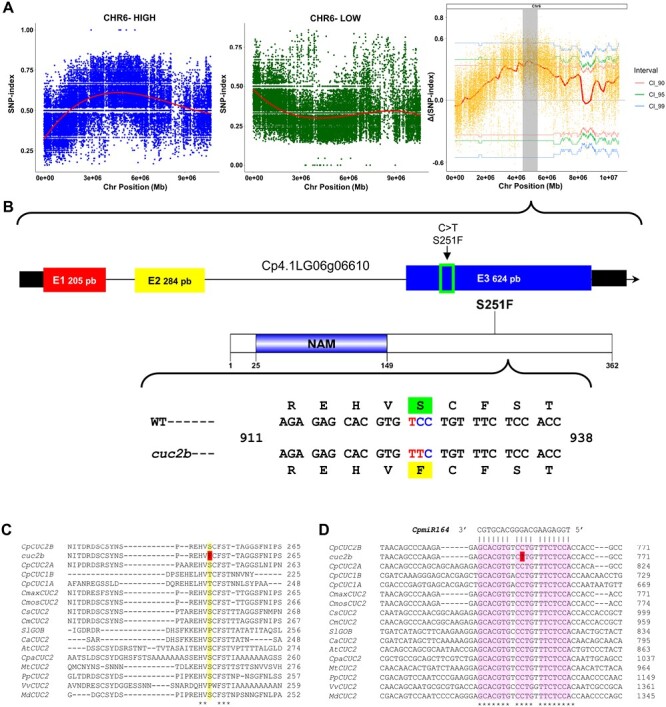
Identification of the cuc2b causal mutation by BSA-seq. (A) SNP index plots of WT and mutant bulks, and the ΔSNP index plot on chromosome 6. The fine mapping of this region allows the identification of an SNP in the candidate region of chromosome 6 as the causal mutation of the cuc2b phenotype. (B) Genomic location of the cuc2b mutation in exon 3 of a NAC-like gene (Cp4.1LG06g06610) in Cucurbita pepo subgenome B. The gene was called CpCUC2B because it is coding for a protein with a high identity to Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor CUC2. (C) The cuc2b mutation causes a change of serine to phenylalanine in residue 251 of CpCUC2B. (D) Multiple alignment of the miR164-binding site in the mRNA sequence of the CUC2 genes of different organisms (Cp, Cucurbita pepo; Cmax, Cucurbita maxima; Cmos, Cucurbita moschata; Cs, Cucumis sativus; Cm, Cucumis melo; Ca, Capsicum annuum; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Cpa, Carica papaya; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Pp, Prunus persica; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Md, Malus domestica). The cuc2b mutation hits a very conserved nucleotide of the miR164-binding site of CpCUC2B.
