Fig. 5.
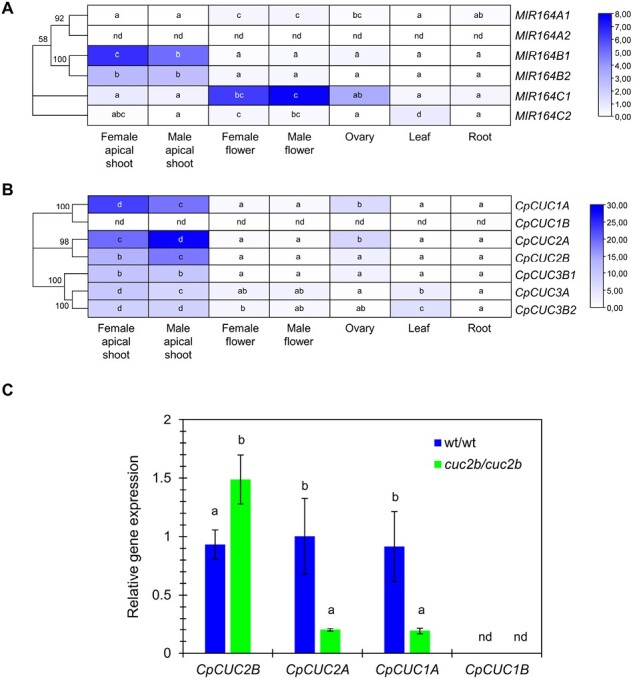
Expression patterns of (A) MIR164 and (B) CpCUC genes in different organs of WT plants: apical shoot at the three (male apical shoot before female flowering) and 12 nodes stage (female apical shoot after female flowering), male and female flowers with a corolla length of 30 mm, ovaries from flowers at the same developmental stage, and leaves of 10 mm and roots from plantlets 17–21 d after germination. FPKM values were used to generate the heatmap with hierarchical clustering analysis. The scale represents the relative signal intensity of the FPKM values. (C) qRT-PCR of CpCUC genes in the apical shoots of WT and cuc2b plants after female flowering. PCR primers for CpCUC genes were designed in the flanking regions of the predicted miR164-binding sites. Different letters indicate significant differences between samples for each gene (ANOVA, P≤0.05); nd, no detectable expression.
