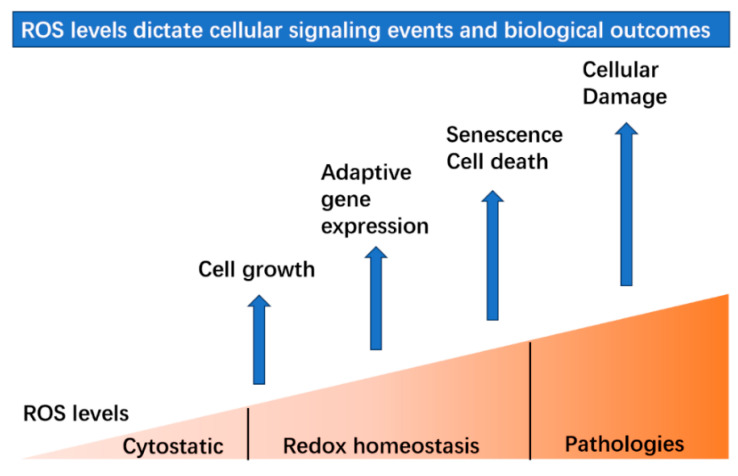
Figure 3.
ROS levels dictate different signaling events and biological outcomes. Within the range of normal physiological levels, ROS participate in many important cellular processes to maintain redox homeostasis. At low levels, ROS promote cell growth by proliferation and differentiation. The induction of ROS levels leads to adaptive gene expression such as the up-regulated expression of antioxidative genes. Then, exposure to higher levels will result in the initiation of senescence or cell death.