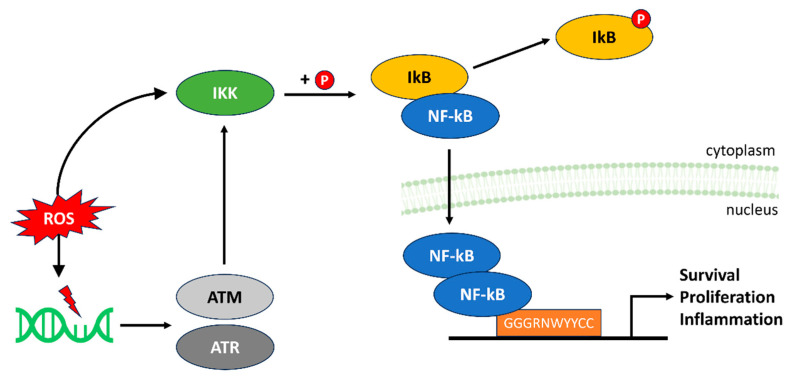
Figure 5.
ROS modulation of the NF-κB pathway. At moderate levels, ROS facilitate NF-κB activation and translocation to the nucleus to initiate gene transcription. This involves the phosphorylation of IkB by IKK (indicated by P), thereby targeting it for ubiquitin-mediated degradation and liberating NF-kB dimers, which translocate to the nucleus. Excessive ROS levels directly and indirectly disrupt IKK regulation, resulting in sustained activation of NF-κB and inflammatory responses.