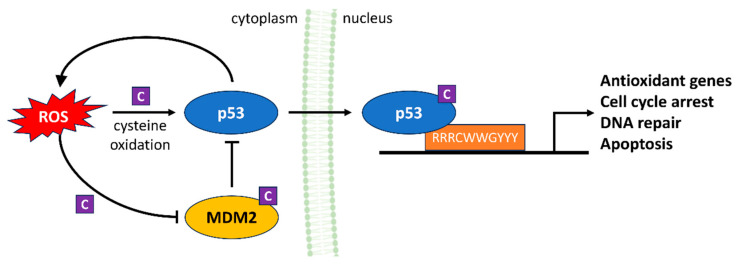
Figure 6.
ROS regulation of the p53 signaling pathway. ROS serve as both triggers and regulators of p53 activation in response to cellular stressors. At physiological concentrations, ROS stabilize and activate p53, promoting DNA repair and antioxidant responses, preventing spreading of damaged cells and keeping ROS at non-toxic levels. These effects of ROS on p53 as well as its regulatory factor MDM2 are mediated by oxidation of cysteine residues in both proteins (C). However, high p53 levels lead to pro-oxidant responses, increasing ROS and suppressing antioxidant genes.