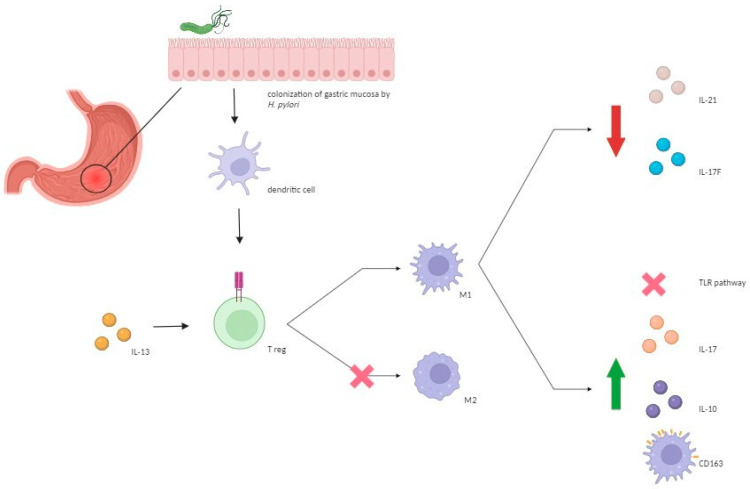
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms underlying the protective role of H. pylori against IBDs. H. pylori induces the modulation of T helper 17/Treg immunological response by inducing a shift from M1 to M2 macrophage lineage which reduces levels of interleukin IL-17F and IL-21, suppresses TLR mediated signaling pathways, and increases the expression of IL-13, IL-10, and CD163, leading to anti-inflammatory effects. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; IL: interleukin; TLR: Toll-like receptor; Treg: regulatory T; M: macrophage.