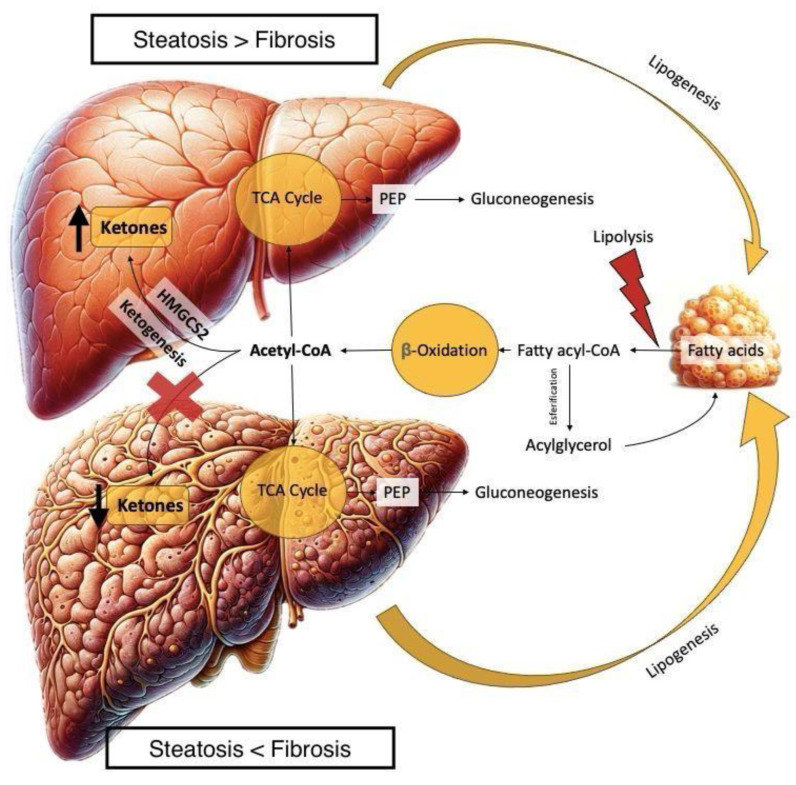
Figure 2.
TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; PEP: Phosphonyl pyruvate. Legend: A dual result of triglyceride exposure might be expected depending on the MASLD status, as a higher exposure to beta-oxidation products leads to a higher production of ketone bodies in the first stages of SLD, while, as fibrosis progresses, ketone metabolism is reduced as a potential early marker of liver metabolic dysfunction [75]. Upward arrows indicate an increase in the synthesis of ketone bodies, activation of the TCA cycle, and gluconeogenesis. Downward arrows would represent a decrease in the processes of lipogenesis and the accumulation of fatty acids. The red cross would indicate the inhibition of the hydroxy-methyl-glutaril-CoA (HMG-CoA) complex pathway, thus decreasing the production of ketone bodies. The red lightning symbol suggests stress or damage leading to steatosis and possibly hepatic fibrosis.