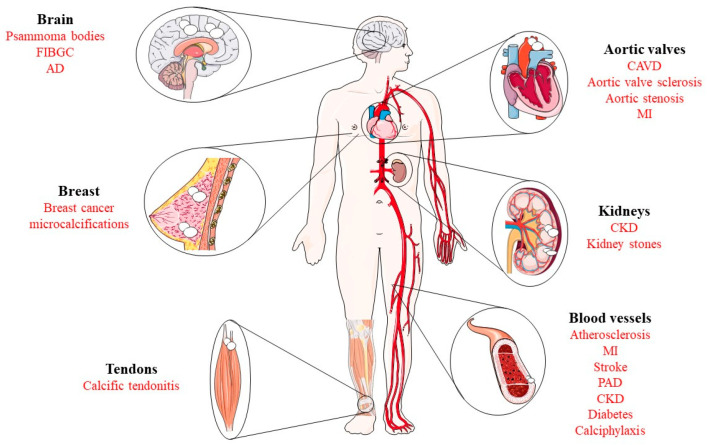
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the main anatomical locations susceptible to the deposition of calcium salts: blood vessels, aortic valves, breast cancer, brain, tendons, or kidneys. In black appear the anatomical locations of calcium deposits and in red the related diseases. FIBGC: familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification, AD: Alzheimer’s disease, CAVD: calcific aortic valve disease, MI: myocardial infarction, CKD: chronic kidney disease, PAD: peripheral artery disease.