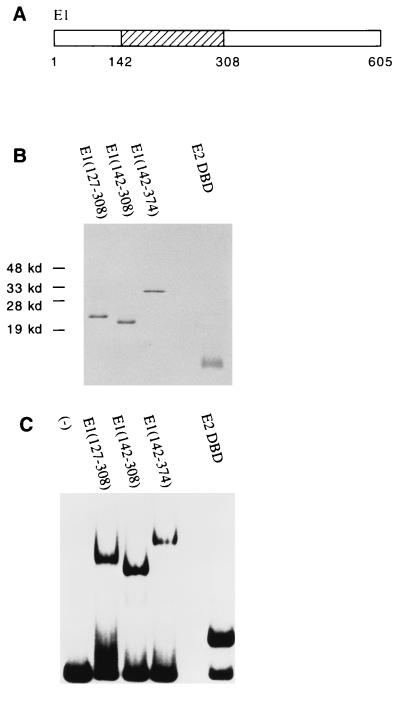
FIG. 1.
DNA-binding activities of the E1 and E2 DBDs. (A) The E1 DBD maps to residues 142 to 308. (B) Analysis by SDS-PAGE (15% gel) and Coomassie staining of 1 μg of protein after the final step of purification. E1(127–308), E1(142–308), and E1(142–374) were expressed as N-terminal GST fusions in E. coli. After affinity purification using glutathione-agarose beads, the E1 fragments were treated with thrombin to remove the GST. The E2 DBD(323–410) was also expressed in E. coli but without any GST fusion. Extracts were then loaded directly onto an S-Sepharose column. Peak fractions were pooled and further purified on a Mono-S column. (C) DNA-binding activity of the purified E1 or E2 DBD protein. Gel mobility shift assays were performed with a probe containing the BPV minimal ori with a high-affinity E2 binding site (BS12H). Ten-microliter binding reaction mixtures containing 12 ng of E1(127–308), 2 ng of E1(142–308), 5 ng of E1(142–374), or 36 pg of E2 DBD(325–410) were incubated for 30 min at room temperature and analyzed on a 5% polyacrylamide gel.