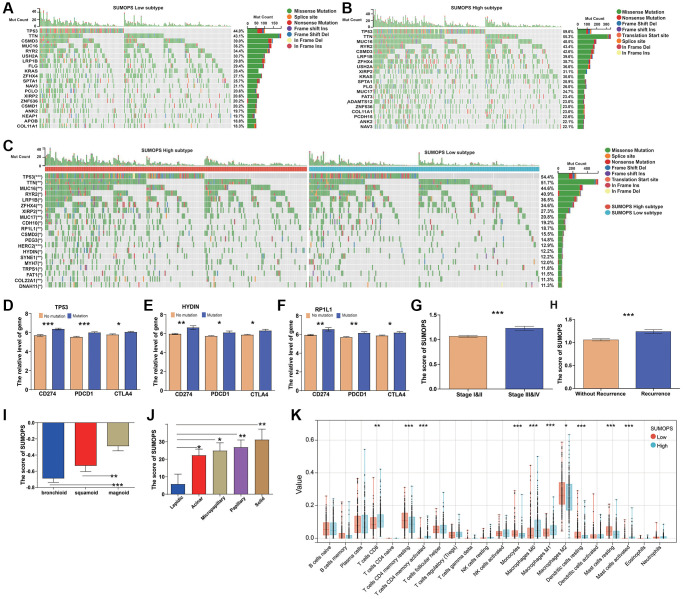
Figure 4.
Relationship between the SUMOPS and genomic alterations as well as molecular subtypes in LUAD. (A, B) Oncoplots showing landscapes of genomic alterations in (A) SUMOPS-low and (B) SUMOPS-high subtypes. (C) Top 20 SUMOPS-related genes with the highest mutation frequency based on TCGA-LUAD cohort. (D) TP53, (E) HYDIN and (F) RP1L1 mutations distinctly facilitated expression of immune checkpoints (CTLA4, CD274, and PDCD1). (G) The score of SUMOPS at different stages. (H) The score of SUMOPS in recurrence and non-recurrence LUAD patients. (I) The score of SUMOPS in different molecular subtypes based on the GSE26939 cohort. (J) The score of SUMOPS in different molecular subtypes based on the GSE58772 cohort. (K) Box plots illustrating the relationships between SUMOPS subtypes and the infiltration of immune cells. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.