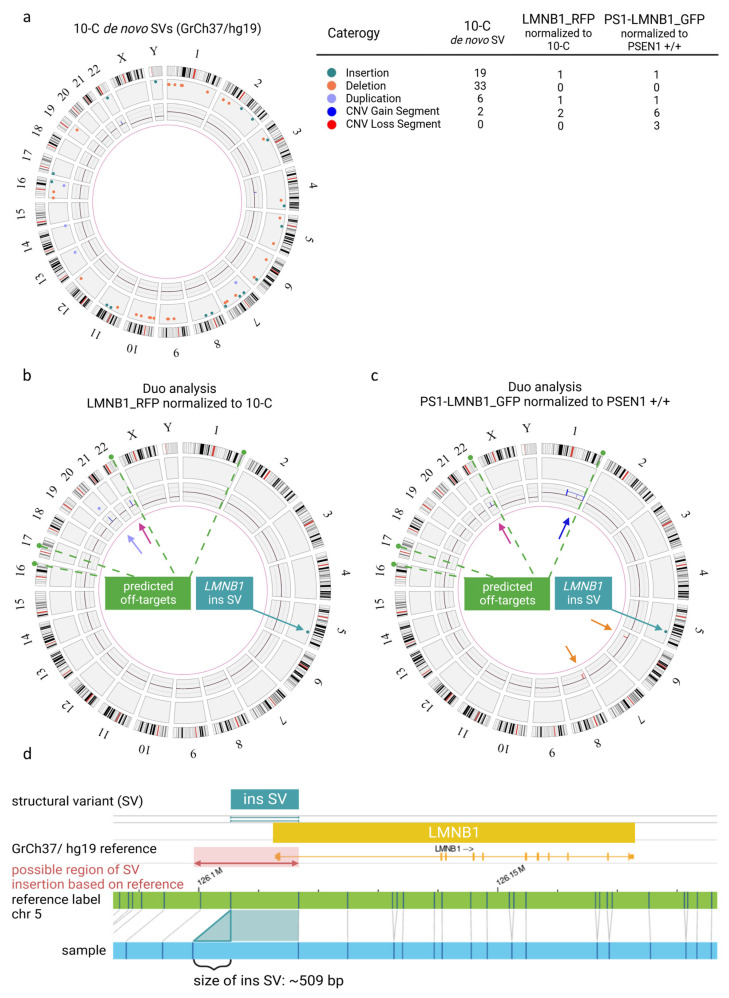
Figure 2.
Quality assessment of genomic integrity in hiPSCs after gene editing and long-term culture using optical genome mapping. (a) Circos plot of 10-C hiPSC line normalized to the human genome reference GrCh37/h19 presenting multiple SVs and CNVs as detailed in the legend. (b) Duo analysis for LMNB_RFP hiPSC normalized to 10 C. The chromosome 22 variant (pink arrow) is detected by CNV pipeline (blue line). The variant on chromosome 20 (purple arrow) is detected by both CNV (blue line) and SV (purple dot). Modification coincident with RFP fluorophore on chromosome 5 (green arrow) is detected by SV pipeline (green dot). (c) Duo analysis for PS1-LMNB_GFP hiPSC normalized to PSEN1 +/+. The chromosome 22 copy number gain (pink arrow) is detected CNV pipeline (blue line). The chromosome 1 variant (dark blue arrow) is detected by CNV pipeline (blue line). Copy number losses on in chromosome 6 and 8 (orange arrows) are detected by CNV (red lines) pipeline. Modification coincident with GFP fluorophore on chromosome 5 (green arrow) is detected as SV (green dot). Predicted off-target sites by CasOFFinder tool are indicated in (b) and (c) (green dashed line). (d) Detail view of insertion on chromosome 5 in LMNB1 gene.