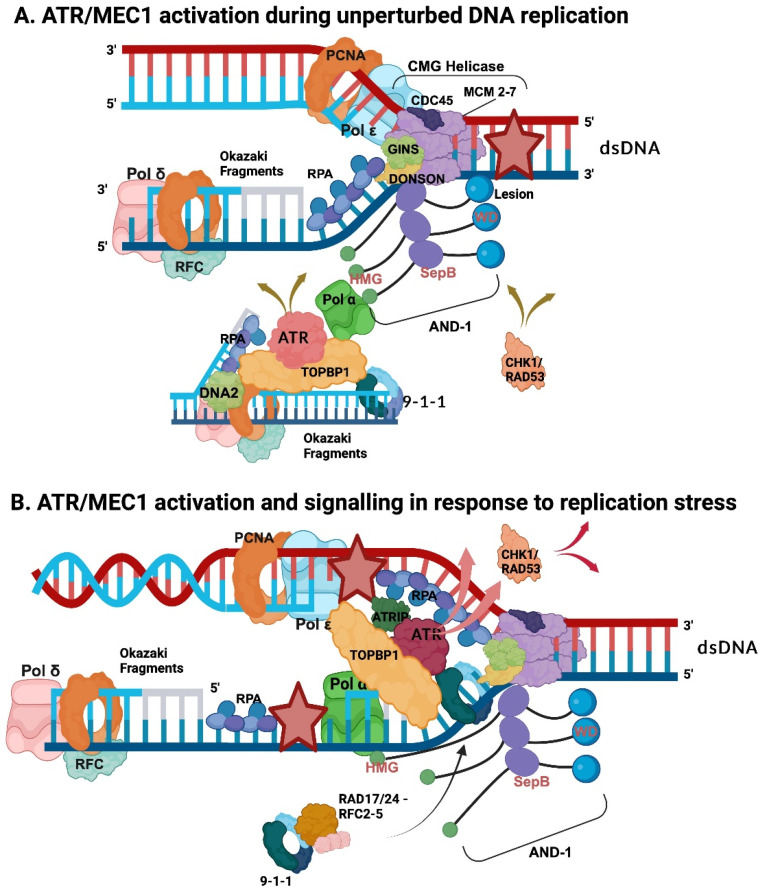
Figure 3.
Signalling at unperturbed and perturbed replication forks. In these simplified RF models, ATR/MEC1 and CHK1/RAD53 initiate signalling pathways at RFs prior to and after passing damaged DNA resulting in stalled leading strand synthesis in the case of DNA damage, which is summarised in panels (A) and (B), respectively. In panel A, during normal, unperturbed replication processes at RFs, the Okazaki fragment synthesis on the lagging strand produces a signal via ATR/MEC1 (light red) and CHK1/RAD53 (dark pink) to slow down the RF by modulating, e.g., the CMG helicase, to synchronise DNA synthesis and nucleotide synthesis. This ATR/MEC1 activity requires Pol α and DNA2 (Okazaki fragment initiation and maturation) and signals unperturbed RFs [114,116]. When Pol ε on the leading strand encounters a DNA lesion (pink star) or is exposed to nucleotide depletion, the enzyme stops DNA synthesis and disengages with or modulates the CMG complex. Then, the latter continues to unwind DNA yielding stretches of ssDNA, which are boundby RPA. These RPA–ssDNA structures recruit ATRIP and ATR (dark red) to the leading strand, in addition to ATR’s binding via TOPBP1, its main activator, to the lagging strand with Pol α and 9-1-1 as partners (panel B). Additionally, the binding of Pol ε to TOPBP1, which may occur via a binding site of Pol ε to TOPBP1 hidden when associated with the CMG complex, may enhance this DDR signalling. It is important to note that Pol α and the RNA primer synthesis are key for the initiation of replication stress signals via ATR/MEC1 and that at RFs, Pol α does not synthesise RNA primers on the leading strand [34,72,73,117,118]. The brown, pink, and red arrows indicate ATR/MEC1 and CHK1/RAD53 signalling during unperturbed and perturbed DNA replication. This model suggests that ATR signalling requires multiple key partners located on both template strands of a stalled RF. It is important to mention that human and yeast CHK1 are homologues on the sequence level, whereas human CHK2 is the orthologue of yeast RAD53, but regarding the ATR pathway during replication stress, human CHK1 and RAD53 are functionally equivalent [119]. The figure was created with Bio Render using published results [32,72,73,114,116,117,119,120,121,122,123,124].