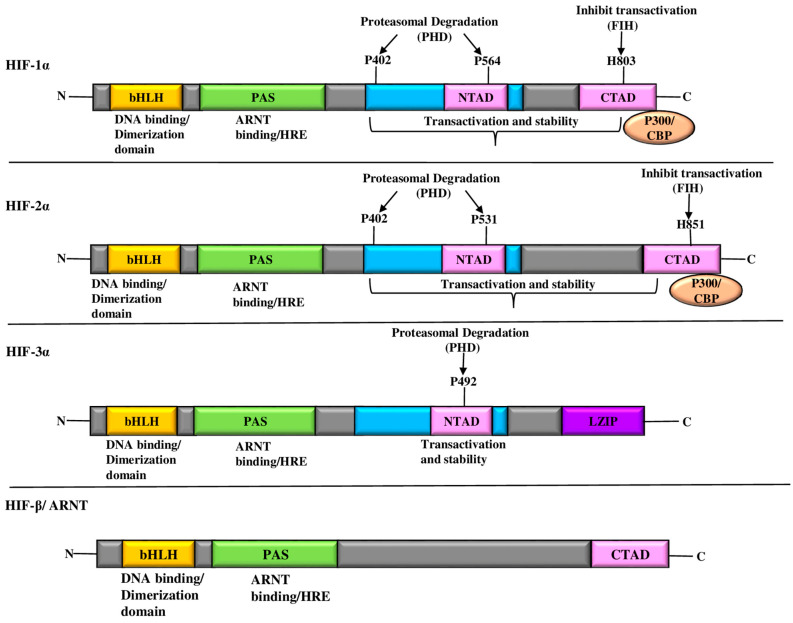
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of the domain structures of HIF. The HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and HIF-3α structural domains along with their transcriptional binding partner, HIF-1β/ARNT, comprise the (HIF-α/HIF-1β) transcriptional complexes. The NH2-terminal region of HIF-α and HIF-1β contains bHLH and PAS domains, which are essential for heterodimerization and DNA binding in the HRE at the target gene loci. HIF-α has two TADs at its COOH-terminus. The ODD domain of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and HIF-3α contains proline(s) residues. HIF-3 has a LZIP domain in the COOH-terminal region; it also lacks the TAD-C domain, unlike HIF-1α, HIF-2α. Abbreviations: ARNT: aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; bHLS-PAS: basic helix loop helix-per ARNT sim; CBP: CREB-binding protein; FIH: factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor; HIF: hypoxia-inducible factor; HRE: hypoxia-responsive element; LZIP: leucine zipper; PHD: prolyl hydroxylase domain; TAD: trans-activation domain.