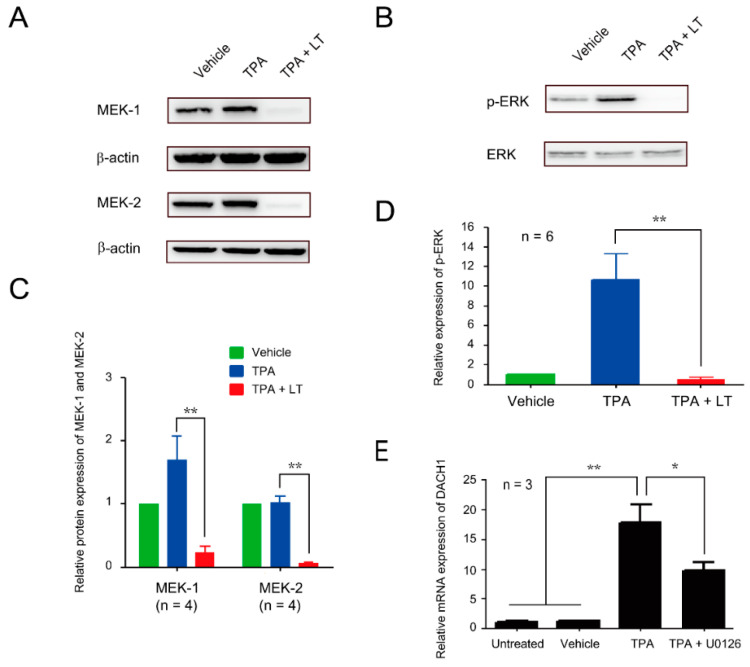
Figure 4.
Involvement of the ERK signaling pathway in DACH1-mediated LT-induced megakaryocytic differentiation suppression. (A) HEL cells were treated with 0.01% DMSO (vehicle), TPA, and TPA combined with LT for 72 h. The total protein extracts were loaded on 10% SDS-PAGE. After transfer to the nitrocellulose paper, the expression levels of MEK-1 and MEK-2 were probed with antibodies against MEK-1 and MEK-2 and detected using Western blot assay, and the relative expression was analyzed (C). β-actin served as the internal control. Full-length blots are presented in Figure S9. (B) The phosphorylated-ERK (p-ERK) expression levels were detected using an antibody against p-ERK and developed through Western blot assay, and the relative expression was calculated (D). ERK was used as the internal control. Full-length blots are presented in Figure S11. (E) The relative expression levels of DACH1 gene mRNA after TPA and U0126 treatments were determined using qRT-PCR. HEL cells untreated or treated with 0.01% DMSO (vehicle) or TPA served as control groups. The mRNA expression level of the DACH1 genes in the untreated group was considered one-fold. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p value < 0.05, ** p value < 0.01, compared with the indicated groups.