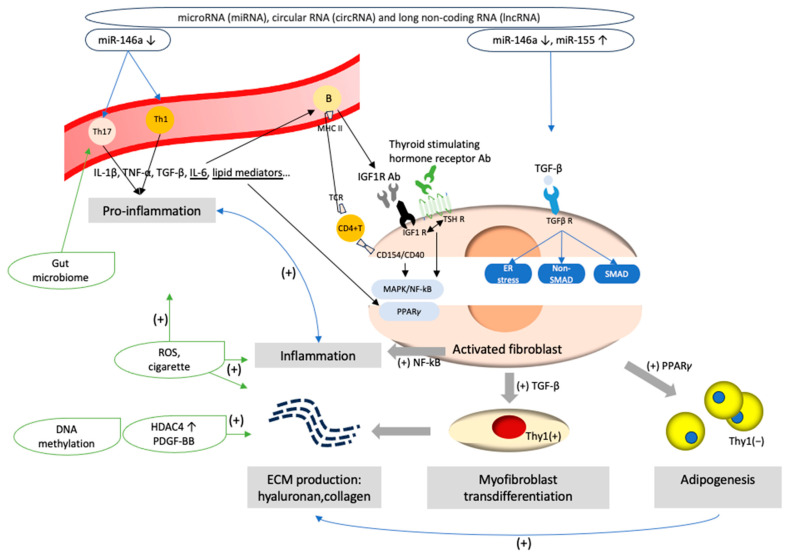
Figure 2.
Pathogenesis of Graves’ ophthalmopathy. (1) Aberrant epigenetic modifications, such as dysregulation of microRNA (miRNA)-146, miRNA 155, circular RNAs and long non-coding RNA, might trigger pro-inflammatory cascades and disturb the expression of signaling molecules critical for myofibroblast transdifferentiation and adipogenesis processes in orbital fibroblasts. (2) The interaction through CD40–CD154 ligation and T cell receptor (TCR)–major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) ligation activates pro-inflammation and orbital fibroblasts with the secretion of inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and lipid mediators. Orbital fibroblasts further upregulate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. IL-6 modulates B cell immunoglobulin secretion. Autoantibodies of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibodies (TSH Ab) interact with their receptors and activate the thyrotropin/IGF-1 receptor complex, promoting the further mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) downstream signaling pathways, which induce orbital fibroblast proliferation and inflammation. (3) The interaction of thyrotropin/IGF-1 receptor complex and lipid mediators upregulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) expression, and induce adipocyte differentiation from Thy1 negative orbital fibroblasts. (4) TGF-β binds to its receptors and activates Smad/non-Smad transcription factors. Thy1 positive orbital fibroblasts are activated and result in myofibroblast transdifferentiation. (5) Contents of the extracellular matrix, such as hyaluronan (HA) or collagen, are produced by activated orbital fibroblasts. Aberrant histone modification and DNA methylation, such as the stimulation of platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) and histone deacetylases (HDAC) 4, would promote the mRNA expression of HA production and pro-inflammation. Factors of adipogenesis, such as prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) and PGJ2, enhance ECM production. (6) Cigarette enhances oxidative stress and upregulate TGF-β1, IL-1β, adipogenesis and the fibrosis-related gene expression in orbital fibroblasts. (7) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress promotes fibrogenesis after the stimulation of TGF-β. (8) The gut microbiome may foster an imbalance in Th17 and T regulatory cells and impact the levels of TSH Ab.