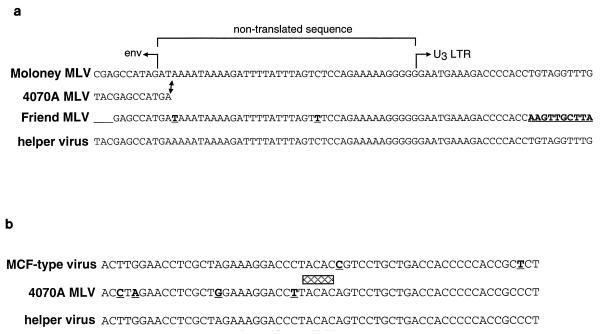
FIG. 4.
Nucleotide sequences at recombination sites in helper virus. (a) Recombination site between 4070A env and MoMLV sequences derived from the pBabeNeo vector. The sequences shown here span the 3′ end of env, the downstream untranslated segment, and the 5′ end of the 3′ LTR. The following sequences are depicted: MoMLV (in the pBabeNeo vector, the neo gene is linked to nontranslated MoMLV sequences 3′ of env), the final 12 coding nucleotides of 4070A env, Friend MLV (in the packaging construct penvAm, present in GP+envAM12 cells, the 3′ end of 4070A env is linked downstream to a sequence derived from Friend MLV), and the sequence of the helper virus. Comparisons of these sequences suggest that a recombination event has occurred between the 3′ end of 4070A env and MoMLV sequences in the untranslated region (from pBabeNeo), as indicated by the arrow. The bases in the Friend MLV sequence which are printed in boldface type and underlined indicate differences compared with the helper virus sequence, suggesting that the Friend MLV sequence does not contribute to the genome of the helper virus. (b) Recombination between endogenous polytropic sequences (which contribute to MCF-type viruses) and 4070A amphotropic virus. Nucleotides 5638 to 5696 of the 5′ LTR–gag-pol PCR-amplified fragment (from Fig. 3b), corresponding to the 3′ portion of pol, are shown and compared with the corresponding sequences from the MCF-type virus pRFM#6 (this represents one of several MCF-type sequences in the database to which the helper virus bears >99% homology at this location) and the 4070A amphotropic retrovirus. The nucleotides which differ between the helper virus and either of these two other viral sequences are underlined and printed in boldface type. The shaded box represents a possible location where recombination between the two viral sequences to form the helper virus sequence may have occurred.