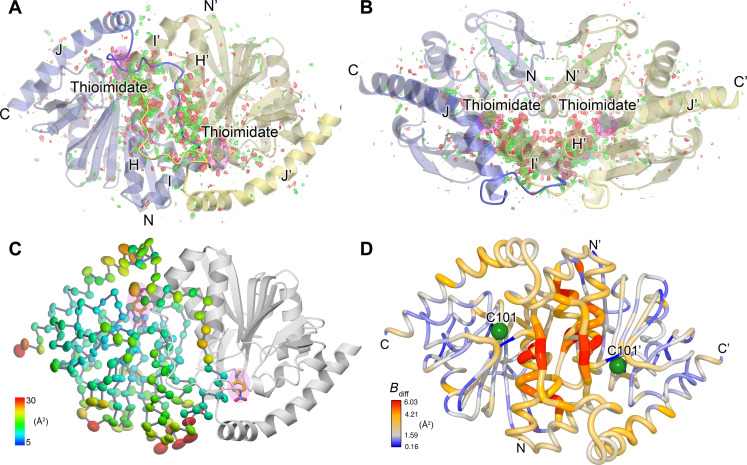
Fig. 4. Catalysis causes global changes to G150T ICH dimer conformational ensemble.
(A and B) Formation of the thioimidate intermediate (labeled; pink highlight) causes changes that propagate across the dimer interface. Two views of the G150T ICH dimer related by a 90° rotation about the horizontal axis are shown. The Fo(30 s)-Fo(0 s) isomorphous difference electron density map is contoured at 3σ (green, positive/red, negative). The linker connecting helices I and J is shown in darker colors and mediates inter-protomer dynamics that connect the active sites. (C) Anisotropic ADP ellipsoids for Cα atoms in the thioimidate intermediate are shown at the 85% probability level and are colored by magnitude, from blue (5 Å2) to red (30 Å2). The thioimidate intermediate (labeled; pink highlight) is near areas of elevated mobility. (D) Formation of the thioimidate intermediate increases mobility in several areas of G150T ICH including the IJ linker and helix H. Difference ADP values between the thioimidate structure and the free enzyme (Bdiff = B30 s − B0 s) are shown, with scale indicated at the lower left. Areas with higher Bdiff values coincide with peaks in the Fo(30 s)-Fo(0 s) isomorphous difference electron density map [(A) and (B)].