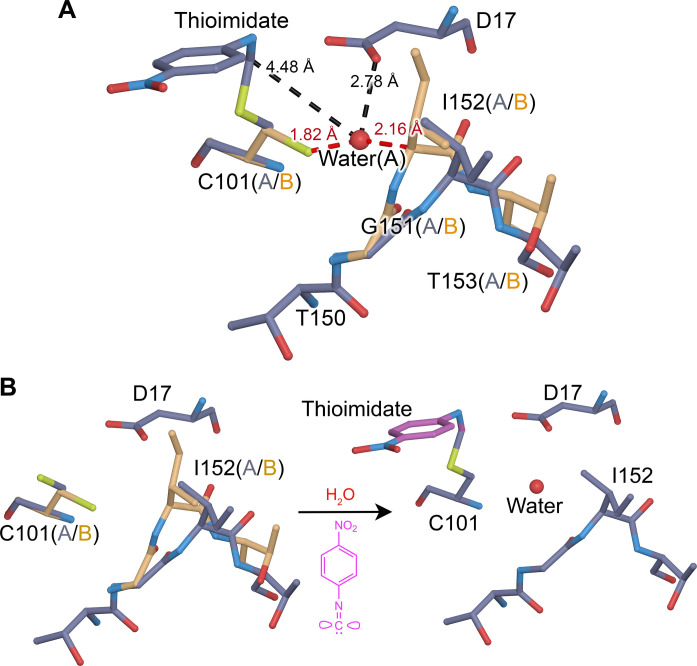
Fig. 5. Thioimidate formation and conformational dynamics facilitate water entry into the active site.
(A) Interactions between the alternate conformations of active site residues and water require correlated motions to avoid steric clashes. The “A” alternate conformation is in slate gray bonds, and the “B” alternate conformation is in gold. Interactions between the partially occupied water (labeled red sphere) and surrounding residues are shown with dotted lines, with distances in angstroms. Red lines indicate steric clashes between the water and residues in the “B” conformation that are avoided by correlated sampling of the nonconflicting alternate “A” conformations. (B) Changes in the conformational heterogeneity of the active site upon thioimidate formation and water entry. Reaction of Cys101 with p-NPIC (purple) forms a thioimidate intermediate (purple) and allows water to enter the active site. If both the thioimidate and water are fully occupied, conformational heterogeneity in the active site is reduced to avoid steric clashes.