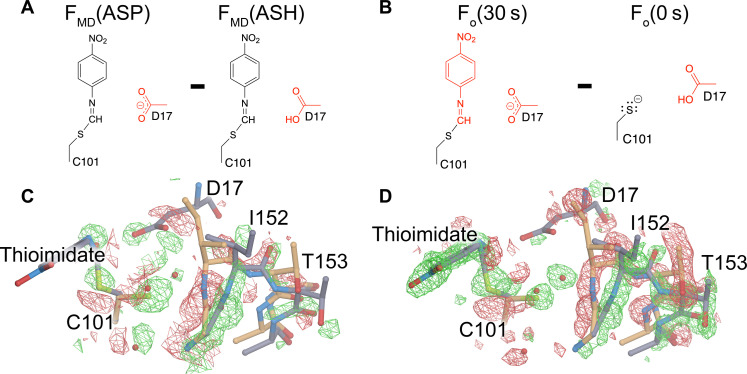
Fig. 6. Deprotonation of Asp17 causes major conformational changes in the active site.
(A) Differing protonation states of Asp17 that were used to calculate structure factors (FMD) in crystalline MD simulations. (B) Corresponding state of the enzyme active site in the experimental Fo(30 s)-Fo(0 s) isomorphous difference electron density map. (C) Calculated isomorphous difference electron density map described in (A) contoured at 6σ. (D) Experimental difference electron density map for the active site contoured at 3σ. The excellent agreement between these maps (C and D) demonstrates that water entry and changes in the active site conformational ensemble upon thioimidate formation are driven by deprotonation of Asp17.